|
Angola
Background:
Civil war has been the norm in Angola since independence from Portugal in 1975.
A 1994 peace accord between the government and the National Union for the Total
Independence of Angola (UNITA) provided for the integration of former UNITA
insurgents into the government and armed forces. A national unity government
was installed in April of 1997, but serious fighting resumed in late 1998,
rendering hundreds of thousands of people homeless. Up to 1.5 million lives may
have been lost in fighting over the past quarter century. The death of
insurgent leader Jonas SAVIMBI in 2002 and a subsequent cease-fire with UNITA
may bode well for the country.
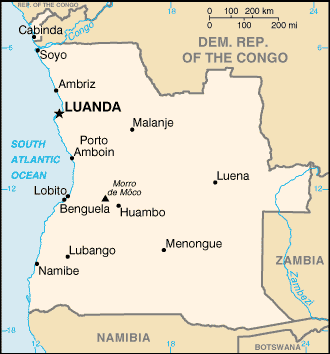
Location:
Location: Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia
and Democratic Republic of the Congo
Area: Total: 1,246,700 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly less than twice the size of Texas
Land boundaries: Total: 5,198 km border countries: Democratic Republic of the
Congo 2,511 km, Republic of the Congo 201 km, Namibia 1,376 km, Zambia 1,110
km.
Coastline: 1,600 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry
season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April.)
Terrain: Narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateau.
Natural resources: Petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar,
gold, bauxite, and uranium.
Geography - note: the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the
rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo
People:
Population: 10,766,471.
Ethnic groups: Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mestico (mixed
European and Native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22%
Religions: indigenous beliefs 47%, Roman Catholic 38%, Protestant 15%.
Languages: Portuguese (official), Bantu and other African languages.
Government:
Government type: Republic, nominally a multiparty democracy with a strong
presidential system.
Capital: Luanda.
Economy overview:
Angola has been an economy in disarray because of a quarter century of nearly
continuous warfare. An apparently durable peace was established after the death
of rebel leader Jonas SAVIMBI on February 22, 2002, but consequences from the
conflict continue including the impact of widespread land mines. Subsistence
agriculture provides the main livelihood for 85% of the population. Oil
production and the supporting activities are vital to the economy, contributing
about 45% to GDP and more than half of exports. Much of the country's food must
still be imported.
Agriculture - products: Bananas, sugarcane, coffee, sisal, corn, cotton, manioc
(tapioca), tobacco, vegetables, plantains; livestock; forest products; fish.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 72,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 25,800.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 21, FM 6, shortwave 7.
Radios: 815,000.
Television broadcast stations: 6.
Televisions: 196,000.
Internet users: 60,000.
Railways: Total: 2,761 km.
Highways: Total: 51,429 km, paved: 5,349 km, unpaved: 46,080 km.
Airports: 243,
with paved runways: 32,
with unpaved runways: 211.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

