|
Belize
Background:
Territorial disputes between the UK and Guatemala delayed the
independence of Belize (formerly British Honduras) until 1981. Guatemala
refused to recognize the new nation until 1992. Tourism has become the mainstay
of the economy. The country remains plagued by high unemployment, growing
involvement in the South American drug trade, and increased urban crime.
Location:
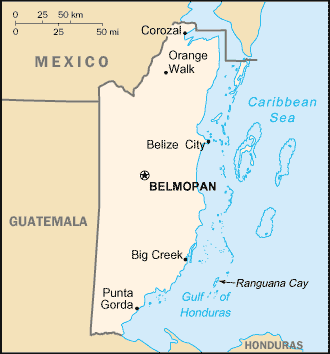
Middle America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Guatemala and
Mexico
Area: Total: 22,966 sq km water: 160 sq km land: 22,806 sq km
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Massachusetts
Land boundaries: Total: 516 km border countries: Guatemala 266 km, Mexico 250
km
Coastline: 386 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; very hot and humid; rainy season (May to November); dry
season (February to May)
Terrain: Flat, swampy coastal plain; low mountains in south
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m highest point: Victoria
Peak 1,160 m
Natural resources: Arable land potential, timber, fish, hydropower
Land use: Arable land: 3% permanent crops: 1% other: 96% (1998 est.)
Geography - note: only country in Central America without a coastline on the
North Pacific Ocean
People:
Population: 262,999 (July 2002 est.)
Ethnic groups: mestizo 48.7%, Creole 24.9%, Maya 10.6%, Garifuna 6.1%, other
9.7%
Religions: Roman Catholic 49.6%, Protestant 27% (Anglican 5.3%, Methodist 3.5%,
Mennonite 4.1%, Seventh-Day Adventist 5.2%, Pentecostal 7.4%, Jehovah's
Witnesses 1.5%), none 9.4%, other 14% (2000)
Languages: English (official), Spanish, Mayan, Garifuna (Carib), Creole
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary democracy
Capital: Belmopan
Economy overview:
The small, essentially private enterprise economy is based
primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism
and construction assuming greater importance. Sugar, the chief crop, accounts
for nearly half of exports, while the banana industry is the country's largest
employer. The government's expansionary monetary and fiscal policies, initiated
in September 1998, led to GDP growth of 6.4% in 1999 and 10.5% in 2000. Growth
decelerated in 2001 to 3% due to the global slowdown and severe hurricane
damage to agriculture, fishing, and tourism. Major concerns continue to be the
rapidly expanding trade deficit and foreign debt. A key short-term objective
remains the reduction of poverty with the help of international donors.
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 18% industry: 24% services: 58%
(2001 est.)
Labor force - by occupation: Agriculture 27%, industry 18%, services 55% (2001
est.)
Agriculture - products: bananas, coca, citrus, sugarcane; lumber; fish,
cultured shrimp
Exports: $239.6 million (f.o.b., 2001 est.)
Exports - commodities: sugar, bananas, citrus, clothing, fish products,
molasses, wood
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 31,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 3,023.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 12.
Radios: 133,000.
Television broadcast stations: 2.
Televisions: 41,000.
Internet users: 15,000.
Highways:. Km paved: 490 km, unpaved: 2,390 km.
Airports - with paved runways: Total: 4, - with unpaved runways: Total: 40.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

