|
Benin
Background:
Dahomey gained its independence from France in 1960; the name was changed to
Benin in 1975. From 1974 to 1989 the country was a socialist state; free
elections were reestablished in 1991.
Location:
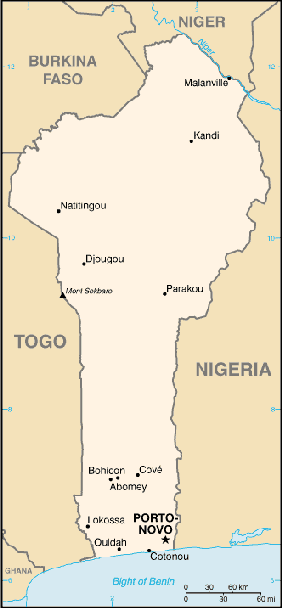
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Nigeria
and Togo
Area: Total: 112,620 sq km, water: 2,000 sq km, land: 110,620 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Pennsylvania.
Land boundaries: Total: 1,989 km, border countries: Burkina Faso 306 km, Niger
266 km, Nigeria 773 km, Togo 644 km.
Coastline: 121 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; hot, humid in south; semiarid in north.
Terrain: Mostly flat to undulating plain; some hills and low mountains.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m, highest point: Mont
Sokbaro 658 m.
Natural resources: Small offshore oil deposits, limestone, marble, timber.
People:
Population: 6,787,625.
Ethnic groups: African 99% (42 ethnic groups, most important being Fon, Adja,
Yoruba, Bariba), Europeans 5,500.
Religions: Indigenous beliefs 50%, Christian 30%, Muslim 20%.
Languages: French (official), Fon and Yoruba (most common vernaculars in
south), tribal languages (at least six major ones in north).
Government:
Government type: Republic under multiparty democratic rule; dropped
Marxism-Leninism December 1989; democratic reforms adopted February 1990;
transition to multiparty system completed 4 April 1991.
Capital: Porto-Novo is the official capital; Cotonou is the seat of government.
Independence: 1 August 1960 (from France).
Economy overview:
The economy of Benin remains underdeveloped and dependent on subsistence
agriculture, cotton production, and regional trade. Growth in real output
averaged a stable 5% in the past five years, but rapid population rise offset
much of this increase. Inflation has subsided over the past several years. In
order to raise growth still further, Benin plans to attract more foreign
investment, place more emphasis on tourism, facilitate the development of new
food processing systems and agricultural products, and encourage new
information and communication technology. The 2001 privatization policy should
continue in telecommunications, water, electricity, and agriculture in spite of
initial government reluctance. The Paris Club and bilateral creditors have
eased the external debt situation.
Statistics:
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 36%, industry: 14%, services: 50%.
Telephones - main lines in use: 51,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 55,500.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 9, shortwave 4.
Radios: 660,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 66,000.
Internet users: 25,000.
Railways: Total: 578 km.
Highways: Total: 6,787 km, paved: 1,357 km, unpaved: 5,430 km.
Airports: 5,
with paved runways: 1,
with unpaved runways: 4.
Return to Visiting Locations
|



