|
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Background:
Bosnia and Herzegovina's declaration of sovereignty in October 1991, was
followed by a declaration of independence from the former Yugoslavia on 3 March
1992 after a referendum boycotted by ethnic Serbs. The Bosnian Serbs -
supported by neighboring Serbia and Montenegro - responded with armed
resistance aimed at partitioning the republic along ethnic lines and joining
Serb-held areas to form a "greater Serbia." In March 1994, Bosniaks and Croats
reduced the number of warring factions from three to two by signing an
agreement creating a joint Bosniak/Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
In 1995-96, a
NATO-led international peacekeeping force (IFOR) of 60,000 troops served in
Bosnia to implement and monitor the military aspects of the agreement.
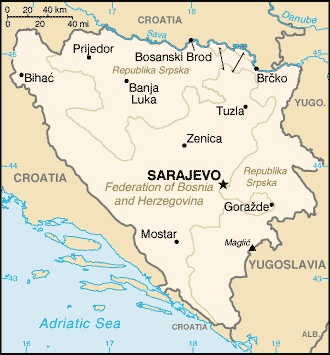
Location:
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Croatia
Area: Total: 51,129 sq km water: 0 sq km land: 51,129 sq km
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than West Virginia.
Land boundaries: Total: 1,459 km, border countries: Croatia 932 km, Yugoslavia
527 km ,
Coastline: 20 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Hot summers and cold winters; areas of high elevation have short, cool
summers and long, severe winters; mild, rainy winters along coast.
Terrain: Mountains and valleys.
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m, highest point: Maglic
2,386 m.
Natural resources: coal, iron, bauxite, manganese, forests, copper, chromium,
lead, zinc, hydropower
People:
Population: 3,964,388.
Ethnic groups: Serb 31%, Bosniak 44%, Croat 17%, Yugoslav 5.5%, other 2.5%.
Religions: Muslim 40%, Orthodox 31%, Roman Catholic 15%, Protestant 4%, other
10%.
Languages: Croatian, Serbian, Bosnian.
Government:
Government type: Emerging federal democratic republic.
Capital: Sarajevo.
Independence: 1 March 1992 (from Yugoslavia).
Economy overview:
Bosnia and Herzegovina ranked next to The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
as the poorest republic in the old Yugoslav federation. Although agriculture is
almost all in private hands, farms are small and inefficient, and the republic
traditionally is a net importer of food. Industry has been greatly overstaffed,
one reflection of the socialist economic structure of Yugoslavia. TITO had
pushed the development of military industries in the republic with the result
that Bosnia hosted a large share of Yugoslavia's defense plants.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 16% industry: 28% services: 56%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 303,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 9,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 8, FM 16.
Radios: 940,000.
Television broadcast stations: 33.
Internet users: 3,500.
Railways: Total: 1,021 km.
Highways: Total: 21,846 km, paved: 14,020 km.
Airports: 27.
Airports - with paved runways: 8, with unpaved runways: 19.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

