|

Burma (Also Known as Myanmar)
Background:
Britain conquered Burma over a period of 62 years (1824-1886) and incorporated
it into its Indian Empire. Burma was administered as a province of India until
1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony; independence outside of
the Commonwealth was attained in 1948. Gen. NE WIN dominated the government
from 1962 to 1988, first as military ruler, then as president, and later as
political kingmaker. Despite multiparty elections in 1990 that resulted in the
main opposition party winning a decisive victory, the ruling military junta
refused to hand over power.
Location:
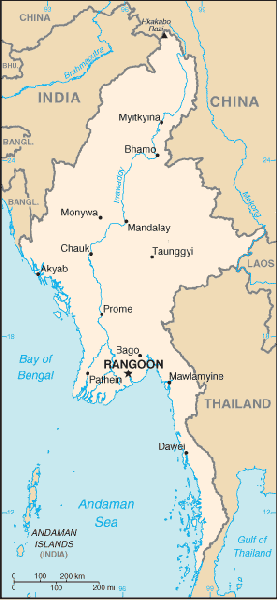
Location: Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal,
between Bangladesh and Thailand.
Area: Total: 678,500 sq km, land: 657,740 sq km, water: 20,760 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Texas.
Land boundaries: Total: 5,876 km, border countries: Bangladesh 193 km, China
2,185 km, India 1,463 km, Laos 235 km, Thailand 1,800 km.
Coastline: 1,930 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest
monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures,
lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April)
Terrain: Central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands.
People:
Population: 42,510,537.
Ethnic groups: Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Indian
2%, Mon 2%, other 5%.
Religions: Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim
4%, animist 1%, other 2%.
Languages: Burmese, minority ethnic groups have their own languages.
Country name: Local short form: Myanma Naingngandaw. Since 1989 the military
authorities in Burma have promoted the name Myanmar; this decision was not
approved by any sitting legislature in Burma, and the US did not adopt the name.
Government:
Government did not adopt the name.
Government type: Military regime.
Capital: Rangoon (regime refers to the capital as Yangon).
Economy overview:
Burma is a resource-rich country that suffers from abject rural poverty. The
military regime took steps in the early 1990s to liberalize the economy after
decades of failure under the "Burmese Way to Socialism", but those efforts have
since stalled. Most
overseas development assistance ceased after the junta suppressed the democracy
movement in 1988 and subsequently ignored the results of the 1990 election.
Burma is data poor, and official statistics are often dated and inaccurate.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 250,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 8,492.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 3, shortwave 3.
Radios: 4.2 million.
Television broadcast stations: 2.
Televisions: 320,000.
Internet users: 10,000, as of September 2000, Internet connections were legal
only for the government, tourist offices, and a few large businesses
Railways: Total: 3,955 km.
Highways: Total: 28,200 km, paved: 3,440 km, unpaved: 24,760 km.
Waterways: 12,800 km note: 3,200 km navigable by large commercial vessels
Airports - with paved runways: 8,
with unpaved runways: 72.
Heliports: 1
Return to Visiting Locations
|

