|
Cameroon
Background:
The former French Cameroon and part of British Cameroon merged in 1961 to form
the present country. Cameroon has generally enjoyed stability, which has
permitted the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a
petroleum industry. Despite movement toward democratic reform, political power
remains firmly in the hands of an ethnic oligarchy.
Location:
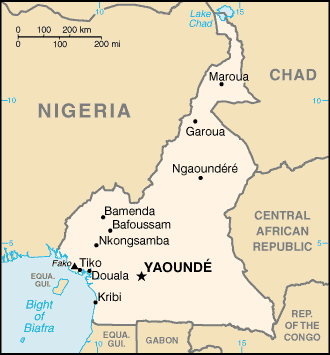
Location: Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial
Guinea and Nigeria
Area: Total: 475,440 sq km, water: 6,000 sq km, land: 469,440 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than California.
Land boundaries: Total: 4,591 km, border countries: Central African Republic
797 km, Chad 1,094 km, Republic of the Congo 523 km, Equatorial Guinea 189 km,
Gabon 298 km, Nigeria 1,690 km.
Coastline: 402 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in
north.
Terrain: Diverse, with coastal plain in southwest, dissected plateau in center,
mountains in west, plains in north.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m, highest point: Fako (on
Cameroon Mountain) 4,095 m.
Natural resources: Petroleum, bauxite, iron ore, timber, hydropower
Land use: Arable land: 12.81%, permanent crops: 2.58% , other: 84.61%.
Natural hazards: Volcanic activity with periodic releases of poisonous gases
from Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun volcanoes.
People:
Population: 15,746,179.
Ethnic groups: Cameroon Highlanders 31%, Equatorial Bantu 19%, Kirdi 11%,
Fulani 10%, Northwestern Bantu 8%, Eastern Nigritic 7%, other African 13%,
non-African less than 1%.
Religions: Indigenous beliefs 40%, Christian 40%, Muslim 20%.
Languages: 24 major African language groups, English (official), French
(official).
Government:
Government type: Unitary republic; multiparty presidential regime (opposition
parties legalized in 1990). note: preponderance of power remains with the
president.
Capital: Yaounde.
Independence: 1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship).
Economy overview:
Because of its oil resources and favorable agricultural conditions, Cameroon
has one of the best-endowed primary commodity economies in sub-Saharan Africa.
Still, it faces many of the serious problems facing other underdeveloped
countries, such as a top-heavy civil service and a generally unfavorable
climate for business enterprise.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 46%, industry: 21%, services: 33%.
Industries: Petroleum production and refining, food processing, light consumer
goods, textiles, lumber.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 95,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 300,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 9, shortwave 3.
Radios: 2.27 million.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 450,000.
Internet users: 45,000.
Railways: 1,008 km.
Highways: Total: 34,300 km, paved: 4,288 km, unpaved: 30,012 km.
Waterways: 2,090 km (of decreasing importance).
Airports: 49. with paved runways: total: 11, with unpaved runways: total: 38.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

