|
Cape Verde
Background:
The uninhabited islands were discovered and colonized by the Portuguese in the
15th century; they subsequently became a trading center for African slaves and
later an important coaling and resupply stop for whaling and transatlantic
shipping. Following independence in 1975, and a tentative interest in
unification with Guinea-Bissau, a one-party system was established and
maintained until multi-party elections were held in 1990. Cape Verde continues
to exhibit one of Africa's most stable democratic governments. Repeated
droughts during the second half of the 20th century caused significant hardship
and prompted heavy emigration. As a result, Cape Verde's expatriate population
is greater than its domestic one. Most Cape Verdeans have both African and
Portuguese antecedents.
Location:
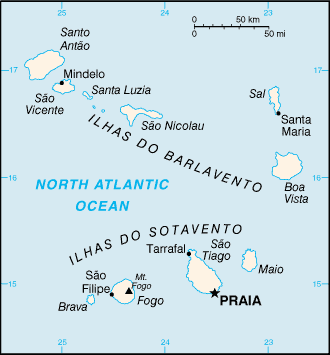
Location: Western Africa, group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, west of
Senegal.
Area: Total: 4,033 sq km, water: 0 sq km, land: 4,033 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than Rhode Island.
Coastline: 965 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate; warm, dry summer; precipitation meager and very errati.c
Terrain: Steep, rugged, rocky, and volcanic.
Natural resources: Salt, basalt rock, limestone, kaolin, fish.
Natural hazards: Prolonged droughts; seasonal harmattan wind produces obscuring
dust; volcanically and seismically active.
Geography - note: Strategic location 500 km from west coast of Africa near
major north-south sea routes; important communications station; important sea
and air refueling site.
People:
Population: 412,137.
Ethnic groups: Creole (mulatto) 71%, African 28%, European 1%.
Religions: Roman Catholic (infused with indigenous beliefs); Protestant (mostly
Church of the Nazarene).
Languages: Portuguese, Crioulo (a blend of Portuguese and West African words).
Government:
Republic.
Capital: Praia.
Independence: 5 July 1975 (from Portugal).
Economy overview:
This island economy suffers from a poor natural resource base, including
serious water shortages exacerbated by cycles of long-term drought. The economy
is service-oriented, with commerce, transport, tourism, and public services
accounting for 72% of GDP. Although nearly 70% of the population lives in rural
areas, the share of agriculture in GDP in 2001 was only 11%, of which fishing
accounts for 1.5%. About 82% of food must be imported. The fishing potential,
mostly lobster and tuna, is not fully exploited. Cape Verde annually runs a
high trade deficit, financed by foreign aid and remittances from emigrants;
remittances supplement GDP by more than 20%. Economic reforms are aimed at
developing the private sector and attracting foreign investment to diversify
the economy. Prospects for 2003 depend heavily on the maintenance of aid flows,
tourism, remittances, and the momentum of the government's development program.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 60,935.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 28,119.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 0, FM 15 (and 17 repeaters).
Radios: 100,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1 (and 7 repeaters).
Televisions: 15,000.
Internet users: 12,000.
Highways: Total: 1,100 km, paved: 858 km. unpaved: 242 km.
Waterways: none
Airports - with paved runways: 6.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

