|
Chile
Background:
A three-year-old Marxist government was overthrown in 1973 by a dictatorial
military regime led by Augusto Pinochet, who ruled until a freely elected
president was installed in 1990. Sound economic policies, first implemented by
the Pinochet dictatorship, led to unprecedented growth in 1991-97 and have
helped secure the country's commitment to democratic and representative
government.
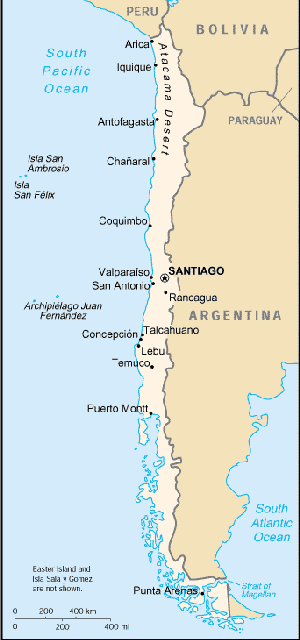
Location:
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean and South
Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru
Area: Total: 756,950 sq km, land: 748,800 sq km, note: includes Easter Island
(Isla de Pascua) and Isla Sala y Gomez, water: 8,150 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than twice the size of Montana
Land boundaries: Total: 6,171 km, border countries: Argentina 5,150 km,
Bolivia 861 km, Peru 160 km.
Coastline: 6,435 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate; desert in north; Mediterranean in central region; cool and
damp in south.
Terrain: Low coastal mountains; fertile central valley; rugged Andes in east.
Natural resources: Copper, timber, iron ore, nitrates, precious metals,
molybdenum, hydropower.
People:
Population: 15,498,930.
Ethnic groups: White and white-Amerindian 95%, Amerindian 3%, other 2%.
Religions: Roman Catholic 89%, Protestant 11%, Jewish NEGL%.
Languages: Spanish.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Santiago.
Independence: 18 September 1810 (from Spain.)
Economy overview:
Chile has a market-oriented economy characterized by a high level of foreign
trade. During the early 1990s, Chile's reputation as a role model for economic
reform was strengthened when the democratic government of Patricio AYLWIN -
which took over from the military in 1990 - deepened the economic reform
initiated by the military government. Growth in real GDP averaged 8% during
1991-97, but fell to half that level in 1998 because of tight monetary policies
implemented to keep the current account deficit in check and because of lower
export earnings - the latter a product of the global financial crisis. A severe
drought exacerbated the recession in 1999, reducing crop yields and causing
hydroelectric shortfalls and electricity rationing, and Chile experienced
negative economic growth for the first time in more than 15 years. Despite the
effects of the recession, Chile maintained its reputation for strong financial
institutions and sound policy that have given it the strongest sovereign bond
rating in South America.
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 8%, industry: 38%, services: 54%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 2.603.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 944,225.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 180 (eight inactive), FM 64.
Radios: 5.18 million.
Television broadcast stations: 63.
Televisions: 3.15 million.
Internet users: 1.75 million.
Railways: total: 6,702 km.
Highways: Total: 79,800 km, paved: 11,012 km, unpaved: 68,788 km.
Airports: 363, with paved runways: 70, with unpaved runways: 293.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

