|
Christmas Island (Also known as Kiritmati in the Territory of Kiribati)
Background:
Named in 1643 for the day of its discovery, the island was annexed
and settlement was begun by the UK in 1888. Phosphate mining began in the
1890s. The UK transferred sovereignty to Australia in 1958. The phosphate mine,
closed in 1987, was reopened four years later, but the need for an alternative
industry has spurred investment in tourism. Old mining areas are being
restored, and almost two-thirds of the island has been declared a national
park.
Location:
Southeastern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of Indonesia. Geographic
coordinates: 10 30 S, 105 40 E. Map references: Southeast Asia. Area: total:
135 sq km land: 135 sq km. Area - comparative: about 0.7 times the size of
Washington, DC. Coastline: 138.9 km. Natural hazards: the narrow fringing reef
surrounding the island can be a maritime hazard
Climate and Terrain:
Tropical; heat and humidity moderated by trade winds. Steep cliffs along coast
rise abruptly to central plateau. Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Indian
Ocean 0 m highest point: Murray Hill 361 m.
People:
Population: 2,771 (July 2001 est.)
Population growth rate: 7.77% (2001 est.)
Ethnic groups: Chinese 61%, Malay 25%, European 11%, other 3%, no indigenous
population.
Religions: Buddhist 55%, Christian 15%, Muslim 10%, other 20% (1991).
Languages: English, Chinese, Malay.
Government:
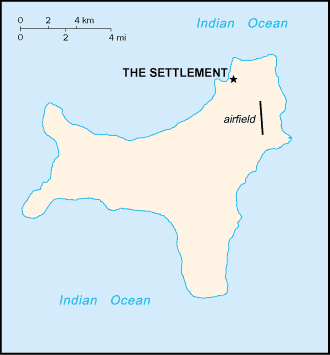
Capital: The Settlement.
Dependency status: Territory of Australia; administered from Canberra by the
Australian Department of the Environment, Sport, and Territories.
Economy overview:
Phosphate mining had been the only significant economic
activity, but in December 1987 the Australian Government closed the mine. In
1991, the mine was reopened by union workers. With the support of the
government, Australian-based Casinos Austria International Ltd. built a $34
million casino on Christmas Island, which opened in 1993. As of yearend 1999,
gaming facilities at the casino were temporarily closed but were expected to
reopen in early 2000. Another economic prospect is the possible location of a
space-launching site on the island. Labor force - by occupation: tourism 400
people, mining 100 people (1995). Industries: tourism, phosphate extraction
(near depletion)
Statistics:
Telephones - mobile cellular: 0.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 1, shortwave 0.
Radios: 1,000).
Railways: 24 km to serve phosphate mines.
Highways: total: 140 km (not including 100 km that is maintained by private.
industry) paved: 30 km unpaved: 110 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|