|
Comoros
Background:
Unstable Comoros has endured 19 coups or attempted coups since gaining
independence from France in 1975. In 1997, the islands of Anjouan and Moheli
declared their independence from Comoros. In 1999, military chief Col. AZALI
seized power. He pledged to resolve the secessionist crisis through a
confederal arrangement named the 2000 Fomboni Accord. In December 2001, voters
approved a new constitution and presidential elections took place in the spring
of 2002. Each island in the archipelago elected its own president and a new
union president was sworn in on May 26, 2002.
Location:
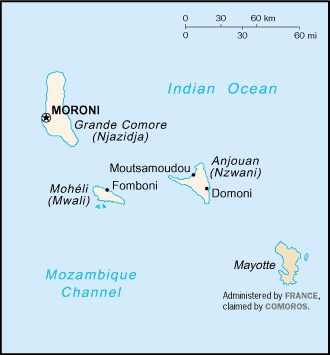
Location: Southern Africa, group of islands at the northern mouth of the
Mozambique Channel, about two-thirds of the way between northern Madagascar and
northern Mozambique.
Area: Total: 2,170 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than 12 times the size of Washington, DC.
Coastline: 340 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical marine; rainy season (November to May).
Terrain: Volcanic islands, interiors vary from steep mountains to low hills.
People:
Population: 632,948.
Ethnic groups: Antalote, Cafre, Makoa, Oimatsaha, Sakalava.
Religions: Sunni Muslim 98%, Roman Catholic 2%.
Languages: Arabic (official), French (official), Shikomoro (a blend of Swahili
and Arabic).
Airports - with paved runways: 4.
Government:
Government type: Independent republic
Capital: Moroni.
Independence: 6 July 1975 (from France).
Economy overview:
One of the world's poorest countries, Comoros is made up of three islands that
have inadequate transportation links, a young and rapidly increasing
population, and few natural resources. The low educational level of the labor
force contributes to a subsistence level of economic activity, high
unemployment, and a heavy dependence on foreign grants and technical
assistance. Agriculture, including fishing, hunting, and forestry, contributes
40% to GDP, employs 80% of the labor force, and provides most of the exports.
The country is not self-sufficient in food production; rice, the main staple,
accounts for the bulk of imports. The government - which is hampered by
internal political disputes - is struggling to upgrade education and technical
training, to privatize commercial and industrial enterprises, to improve health
services, to diversify exports, to promote tourism, and to reduce the high
population growth rate.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 7,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 4, shortwave 1.
Radios: 90,000.
Televisions: 1,000.
Internet users: 2,500.
Railways: 0 km
Highways: Total: 880 km, paved: 673 km. unpaved: 207 km.
Airports: 4 (2002)
Return to Visiting Locations
|