|
Republic of Congo
Background:
Upon independence in 1960, the former French region of Middle Congo became the
Republic of the Congo. A quarter century of experimentation with Marxism was
abandoned in 1990 and a democratically elected government installed in 1992. A
brief civil war in 1997 restored former Marxist President Sassou-Nguesso, but
ushered in a period of ethnically based unrest. Southern-based rebel groups
agreed to a final peace accord in March 2003. The Republic of Congo is one of
Africa's largest petroleum producers with significant potential for offshore
development.
Location:
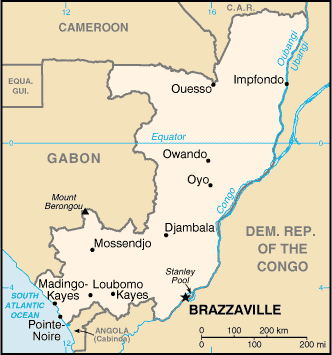
Location: Western Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola
and Gabon.
Area: Total: 342,000 sq km, water: 500 sq km. land: 341,500 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Montana.
Land boundaries: Total: 5,504 km; border countries: Angola 201 km, Cameroon
523 km, Central African Republic 467 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,410
km, Gabon 1,903 km.
Coastline: 169 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; rainy season (March to June); dry season (June to October);
constantly high temperatures and humidity; particularly enervating climate
astride the Equator.
Terrain: Coastal plain, southern basin, central plateau, northern basin.
People:
Population: 2,954,258.
Ethnic groups: Kongo 48%, Sangha 20%, M'Bochi 12%, Teke 17%, Europeans and
other 3%.
Religions: Christian 50%, animist 48%, Muslim 2%.
Languages: French (official), Lingala and Monokutuba (lingua franca trade
languages).
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Brazzaville.
Independence: 15 August 1960 (from France).
Economy overview:
The economy is a mixture of village agriculture and handicrafts, an
industrial sector based largely on oil, support services, and a government
characterized by budget problems and overstaffing. Oil has supplanted forestry
as the mainstay of the economy, providing a major share of government revenues
and exports. In the early 1980s, rapidly rising oil revenues enabled the
government to finance large-scale development projects with GDP growth
averaging 5% annually, one of the highest rates in Africa. The government has
mortgaged a substantial portion of its oil earnings, contributing to a shortage
of revenues.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 22,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 3,300.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 5, shortwave 3.
Radios: 341,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 33,000.
Internet users: 500.
Railways: Total: 894 km.
Highways: Total: 12,800 km, paved: 1,242 km, unpaved: 11,558 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 4,
with unpaved runways: 27.
Return to Visiting Locations
|