|
Croatia
Background:
In 1918, the Croats, Serbs, and Slovenes formed a kingdom known after 1929
as
Yugoslavia. Following World War II, Yugoslavia became an independent
communist
state under the strong hand of Marshal TITO. Although Croatia
declared its
independence from Yugoslavia in 1991, it took four years of
sporadic, but often
bitter, fighting before occupying Serb armies were
mostly cleared from Croatian
lands. Under UN supervision the last
Serb-held enclave in eastern Slavonia was
returned to Croatia in
1998.
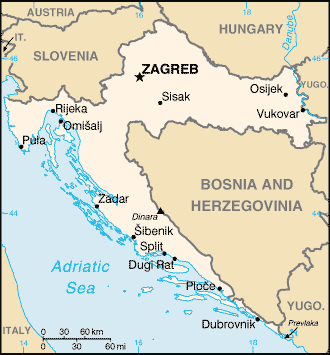
Location:
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea, between Bosnia
and
Herzegovina and Slovenia
Area: Total: 56,542 sq km, water:
128 sq km, land: 56,414 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller
than West Virginia.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,185 km , border countries:
Bosnia and Herzegovina 932
km, Hungary 329 km, Yugoslavia 254 km,
Slovenia 670 km.
Coastline: 5,835 km (mainland 1,777 km, islands 4,058
km).
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Mediterranean and continental; continental climate predominant
with
hot summers and cold winters; mild winters, dry summers along coast.
Terrain: Geographically diverse; flat plains along Hungarian border,
low
mountains and highlands near Adriatic coastline and islands.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m, highest point:
Dinara
1,830 m.
People:
Population: 4,390,751.
Ethnic groups: Croat 78.1%, Serb 12.2%, Bosniak
0.9%, Hungarian 0.5%, Slovene
0.5%, Czech 0.4%, Albanian 0.3%,
Montenegrin 0.3%, Roma 0.2%, others 6.6%.
Religions: Roman Catholic
76.5%, Orthodox 11.1%, Muslim 1.2%, Protestant 0.4%,
others and unknown
10.8%.
Languages: Croatian 96%, other 4% (including Italian, Hungarian,
Czech, Slovak,
and German.)
Government:
Government type: Presidential/parliamentary democracy.
Capital: Zagreb
Independence: 25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia).
Economy overview:
Before the dissolution of Yugoslavia, the Republic of Croatia, after
Slovenia,
was the most prosperous and industrialized area, with a per
capita output
perhaps one-third above the Yugoslav average. The economy
emerged from its mild
recession in 2000 with tourism the main factor, but
massive structural
unemployment remains a key negative element. The
government's failure to press
the economic reforms needed to spur growth
is largely the result of coalition
politics and public resistance,
particularly from the trade unions, to measures
that would cut jobs,
wages, or social benefits.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1,721,139.
Telephones - mobile
cellular: 1.3 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 16, FM 98, shortwave
5.
Radios: 1.51 million.
Television broadcast stations: 36 (plus
321 repeaters).
Televisions: 1.22 million.
Internet
users: 200,000.
Railways: Total: 2,726 km.
Highways: Total: 28,009
km, paved: 23,695 km, unpaved: 4,314 km.
Airports: 67,
with paved
runways: 22,
with unpaved runways: 45. Heliport 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

