|
Czech Republic
Background:
After World War II, Czechoslovakia fell within the Soviet sphere of
influence.
In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts
of the country's
leaders to liberalize party rule and create "socialism
with a human face."
Anti-Soviet demonstrations the following year ushered
in a period of harsh
repression. With the collapse of Soviet authority in
1989, Czechoslovakia
regained its freedom through a peaceful "Velvet
Revolution." On 1 January 1993,
the country underwent a "velvet divorce"
into its two national components, the
Czech Republic and Slovakia. Now a
member of NATO, the Czech Republic has moved
toward integration in world
markets, a development that poses both
opportunities and risks.
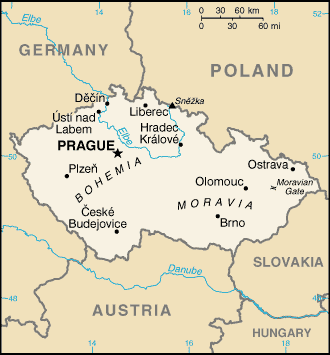
Location:
Central Europe, southeast of Germany.
Area: Total: 78,866 sq km, water:
1,590 sq km, land: 77,276 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller
than South Carolina.
Land boundaries: Total: 1,881 km, border
countries: Austria 362 km, Germany
646 km, Poland 658 km, Slovakia 215
km.
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked).
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
Terrain: Bohemia in the west consists of rolling plains, hills, and
plateaus surrounded by low mountains; Moravia in the east consists of
very hilly country.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Elbe River
115 m, highest point: Snezka
1,602 m .
Natural resources: Hard
coal, soft coal, kaolin, clay, graphite, timber
People:
Population: 10,256,760.
Ethnic groups: Czech 81.2%, Moravian 13.2%,
Slovak 3.1%, Polish 0.6%, German
0.5%, Silesian 0.4%, Roma 0.3%,
Hungarian 0.2%, other 0.5%.
Religions: Atheist 39.8%, Roman Catholic
39.2%, Protestant 4.6%, Orthodox 3%,
other 13.4%.
Languages: Czech.
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary democracy.
Capital: Prague.
Independence: 1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech
Republic and Slovakia).
Economy overview:
Basically one of the most stable and prosperous of the post-Communist states,
the Czech Republic has been recovering from recession since mid-1999. Growth in
2000-01 was led by exports to the EU, especially Germany, and foreign
investment, while domestic demand is reviving. Uncomfortably high fiscal and
current account deficits could be future problems. Unemployment is gradually
declining as job creation continues in the rebounding economy; inflation is up
to 4.7% but still moderate. The EU put the Czech Republic just behind Poland
and Hungary in preparations for accession, which will give further impetus and
direction to structural reform.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 5%,
industry: 41%, services: 54%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 3.869 million.
Telephones - mobile
cellular: 4.346 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 31, FM
304.
Radios: 3,159,134.
Television broadcast
stations: 150.
Televisions: 3,405,834.
Internet users: 1.1
million.
Railways: Total: 9,444 km.
Highways: Total: paved: 55,432
km, unpaved: 0 km.
Airports: 121,
with paved runways: 44,
with unpaved runways: 77.
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|