|
Ecuador
Background:
The "Republic of the Equator" was one of three countries that emerged from the
collapse of Gran Colombia in 1830 (the others being Colombia and Venezuela).
Between 1904 and 1942, Ecuador lost territories in a series of conflicts with
its neighbors. A border war with Peru that flared in 1995 was resolved in 1999.
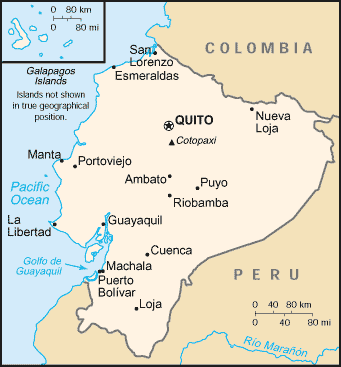
Location:
Western South America, bordering the Pacific Ocean at the Equator, between
Colombia and Peru
Area: Total: 283,560 sq km, note: includes Galapagos Islands, water: 6,720 sq
km, land: 276,840 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Nevada.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,010 km, border countries: Colombia 590 km, Peru
1,420 km.
Coastline: 2,237 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical along coast, becoming cooler inland at higher elevations;
tropical in Amazonian jungle lowlands.
Terrain: Coastal plain, inter-Andean central highlands, and flat to rolling
eastern jungle.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Chimborazo
6,267 m.
Natural resources: Petroleum, fish, timber, hydropower.
People:
Population: 13,447,494.
Ethnic groups: Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 65%, Amerindian 25%,
Spanish and others 7%, black 3%.
Religions: Roman Catholic 95%.
Languages: Spanish (official), Amerindian languages (especially Quechua).
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Quito.
Independence: 24 May 1822 (from Spain).
Economy overview:
Ecuador has substantial oil resources and rich agricultural areas. Because
the country exports primary products such as oil, bananas, and shrimp,
fluctuations in world market prices can have a substantial domestic impact.
Ecuador joined the World Trade Organization in 1996, but has failed to comply
with many of its accession commitments. The aftermath of El Nino and depressed
oil market of 1997-98 drove Ecuador's economy into a free-fall in 1999. The
beginning of 1999 saw the banking sector collapse, which helped precipitate an
unprecedented default on external loans later that year. Continued economic
instability drove a 70% depreciation of the currency throughout 1999, which
forced a desperate government to "dollarization" the currency regime in 2000. The
move stabilized the currency, but did not stave off the ouster of the
government.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 11%, industry: 25%, services: 64%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1,115,272.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 384,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 392, FM 35, shortwave 29.
Radios: 5 million.
Television broadcast stations: 7 (plus 14 repeaters).
Televisions: 2.5 million.
Internet users: 328,000.
Railways: Total: 965 km.
Highways: Total: 43,197 km, paved: 8,165 km, unpaved: 35,032 km.
Airports: 205,
with paved runways: 61,
with unpaved runways: 144.
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

