|
Egypt
Background:
Nominally independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty
following World War II. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the
resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile river in
the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest
in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all
continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled
to ready the economy for the new millennium through economic reform and massive
investment in communications and physical infrastructure.
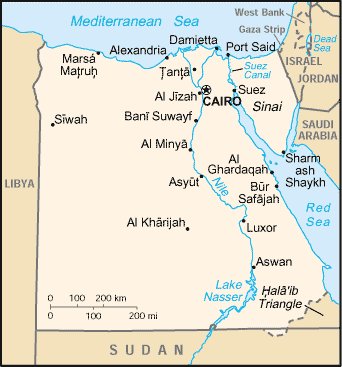
Location:
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Libya and the Gaza
Strip.
Area: Total: 1,001,450 sq km, land: 995,450 sq km, water: 6,000 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than three times the size of New Mexico.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,665 km border countries: Gaza Strip 11 km, Israel
266 km, Libya 1,115 km, Sudan 1,273 km.
Coastline: 2,450 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Desert; hot, dry summers with moderate winters.
Terrain: Vast desert plateau interrupted by Nile valley and delta.
Natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, manganese,
limestone, gypsum, talc, asbestos, lead, zinc.
People:
Population: 70,712,345.
Ethnic groups: Eastern Hamitic stock (Egyptians, Bedouins, and Berbers) 99%,
Greek, Nubian, Armenian, other European (primarily Italian and French) 1%.
Religions: Muslim (mostly Sunni) 94%, Coptic Christian and other 6%.
Languages: Arabic (official), English and French widely understood by educated
classes.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Cairo.
Independence: 28 February 1922 (from UK).
Economy overview:
Egypt improved its macroeconomic performance throughout most of the last
decade by following IMF advice on fiscal, monetary, and structural reform
policies. As a result, Cairo managed to tame inflation, slash budget deficits,
and attract more foreign investment. In the past three years, however, the pace
of reform has slackened, and excessive spending on national infrastructure
projects has widened budget deficits again. Lower foreign exchange earnings
since 1998 resulted in pressure on the Egyptian pound and periodic dollar
shortages. Monetary pressures have increased since 11 September 2001 because of
declines in tourism, Suez canal tolls, and exports, and Cairo has devalued the
pound several times in the past year.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 14%, industry: 30%, services: 56%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 3,971,500.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 380,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 42, FM 14.
Radios: 20.5 million.
Television broadcast stations: 98.
Televisions: 7.7 million.
Internet users: 560,000.
Railways: Total: 4,955 km.
Highways: Total: 64,000 km, paved: 50,000 km, unpaved: 14,000 km.
Airports: 92,
with paved runways: 72,
with unpaved runways: 20.
Heliports: 2.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

