|
Equatorial Guinea
Background:
Equatorial Guinea gained independence in 1968 after 190 years of Spanish rule.
President Obiang Nguem Mbasogo has ruled the tiny country, composed of a
mainland portion plus five inhabited islands and one of the smallest countries
on the African continent, since he seized power in a coup in 1979. Although
nominally a constitutional democracy since 1991, the 1996 and 2002 presidential
elections - as well as the 1999 legislative elections - were widely seen as
being flawed.
Location:
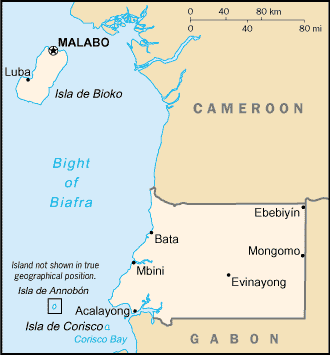
Location: Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Cameroon and
Gabon
Area: Total: 28,051 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Maryland.
Land boundaries: Total: 539 km; border countries: Cameroon 189 km, Gabon 350
km.
Coastline: 296 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; always hot, humid.
Terrain: Coastal plains rise to interior hills; islands are volcanic.
Natural resources: Oil, petroleum, timber, small-unexploited deposits of gold,
manganese, uranium, titanium, iron ore.
People:
Population: 510,473.
Ethnic groups: Bioko (primarily Bubi, some Fernandinos), Rio Muni (primarily
Fang), Europeans less than 1,000, mostly Spanish
Religions: nominally Christian and predominantly Roman Catholic, pagan
practices
Languages: Spanish (official), French (official), pidgin English, Fang, Bubi,
Ibo
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Malabo.
Independence: 12 October 1968 (from Spain).
Economy overview:
The discovery and exploitation of large oil reserves have contributed to
dramatic economic growth in recent years. Forestry, farming, and fishing are
also major components of GDP. Subsistence farming predominates. Although
pre-independence Equatorial Guinea counted on cocoa production for hard
currency earnings, the neglect of the rural economy under successive regimes
has diminished potential for agriculture-led growth (the government has stated
its intention to reinvest some oil revenue into agriculture). A number of aid
programs sponsored by the World Bank and the IMF have been cut off since 1993
because of corruption and mismanagement. Government officials and their family
members, for the most part, own businesses. Undeveloped natural resources
include titanium, iron ore, manganese, uranium, and alluvial gold. Growth will
remain strong in 2003, led by oil.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 6,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 300.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 0, FM 3, shortwave 5.
Radios: 180,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 4,000.
Internet users: 900.
Railways: Total: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 2,880 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 2,
with unpaved runways: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

