|
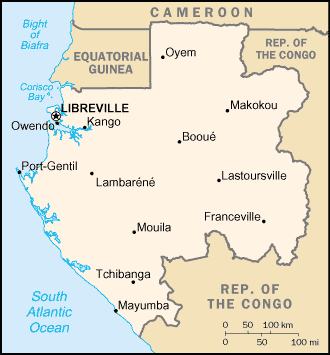
Gabon
Background:
Ruled by autocratic presidents since independence from France in 1960, Gabon
introduced a multiparty system and a new constitution in the early 1990s that
allowed for a more transparent electoral process and for reforms of
governmental institutions. A small population, abundant natural resources, and
considerable foreign support have helped make Gabon one of the more prosperous
black African countries.
Location:
Location: Western Africa, bordering the Atlantic Ocean at the Equator, between
Republic of the Congo and Equatorial Guinea
Area: Total: 267,667 sq km, water: 10,000 sq km, land: 257,667 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Colorado.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,551 km, border countries: Cameroon 298 km, Republic
of the Congo 1,903 km, Equatorial Guinea 350 km.
Coastline: 885 km.
Climate and Terrain:
People:
Population: 1,321,560.
Ethnic groups: Bantu tribes including four major tribal groupings (Fang,
Bapounou, Nzebi, Obamba), other Africans and Europeans 154,000, including
10,700 French and 11,000 persons of dual nationality.
Religions: Christian 55%-75%, animist, Muslim less than 1%.
Languages: French (official), Fang, Myene, Nzebi, Bapounou/Eschira, Bandjabi.
Government:
Government type: Republic; multiparty presidential regime.
Capital: Libreville.
Independence: 17 August 1960 (from France).
Economy overview:
Gabon enjoys a per capita income four times that of most nations of sub-Saharan
Africa. This has supported a sharp decline in extreme poverty; yet because of
high-income inequality a large proportion of the population remains poor. Gabon
depended on timber and manganese until oil was discovered offshore in the early
1970s. The oil sector now accounts for 50% of GDP. Gabon continues to face
fluctuating prices for its oil, timber, and manganese exports. Despite the
abundance of natural wealth, poor fiscal management hobbles the economy.
Devaluation of its Francophone currency by 50% on 12 January 1994 sparked a
one-time inflationary surge, to 35%; the rate dropped to 6% in 1996.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 39,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 120,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 6, FM 7 (and 11 repeaters), shortwave 4.
Radios: 208,000.
Television broadcast stations: 4.
Televisions: 63,000.
Internet users: 18,000.
Railways: Total: 814 km.
Highways: Total: 8,464 km, paved: 838 km, unpaved: 7,626 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 10,
with unpaved runways: 47.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

