|
The Gambia
Background:
The Gambia gained its independence from the UK in 1965; it formed a short-lived
federation of Senegambia with Senegal between 1982 and 1989. In 1991 the two
nations signed a friendship and cooperation treaty. A military coup in 1994
overthrew the president and banned political activity, but a 1996 constitution
and presidential elections, followed by parliamentary balloting in 1997,
completed a nominal return to civilian rule. The country undertook another
round of presidential and legislative elections in late 2001 and early 2002.
Location:
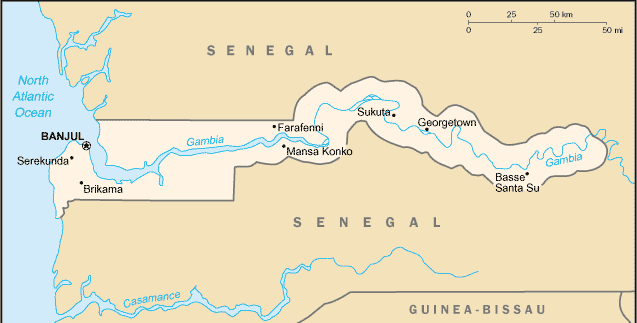
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal.
Area: Total: 11,300 sq km, land: 10,000 sq km, water: 1,300 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly less than twice the size of Delaware
Land boundaries: Total: 740 km, border countries: Senegal 740 km.
Coastline: 80 km.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season.
Terrain: Flood plain of the Gambia River flanked by some low hills.
Natural resources: Fish.
People:
Population: 1,501,050.
Ethnic groups: African 99% (Mandinka 42%, Fula 18%, Wolof 16%, Jola 10%,
Serahuli 9%, other 4%), non-African 1%.
Religions: Muslim 90%, Christian 9%, indigenous beliefs 1%.
Languages: English (official), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous
vernaculars.
Government:
Government type: Republic under multiparty democratic rule.
Capital: Banjul.
Independence: 18 February 1965 (from UK).
Economy overview:
The Gambia has no important mineral or other natural resources and has a
limited agricultural base. About 75% of the population depends on crops and
livestock for its livelihood. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the
processing of peanuts, fish, and hides. The government's 1998 seizure
of the private peanut firm Alimenta eliminated the largest purchaser of Gambian
groundnuts; the following two marketing seasons have seen substantially lower
prices and sales. A decline in tourism in 2000 has also held back growth.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 31,900.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 5,624.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 3, FM 2.
Radios: 196,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 5,000.
Internet users: 5,000.
Railways: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 2,700 km, paved: 956 km, unpaved: 1,744 km.
Airports: 1.
|

