|
Grenada
Background:
One of the smallest independent countries in the western hemisphere, Grenada
was seized by a Marxist military council on 19 October 1983. Six days later the
island was invaded by US forces and those of six other Caribbean nations, which
quickly captured the ringleaders and their hundreds of Cuban advisers. Free
elections were re-instituted the following year.
Location:
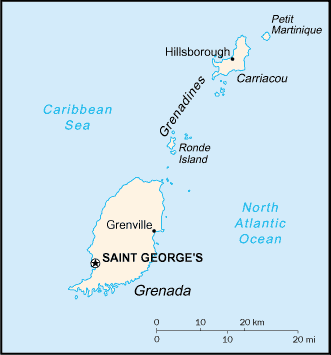
Location: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean, north
of Trinidad and Tobago.
Area: Total: 344 sq km.
Area - comparative: Twice the size of Washington, DC.
Coastline: 121 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; tempered by northeast trade winds.
Terrain: Volcanic in origin with central mountains.
Natural resources: Timber, tropical fruit, deepwater harbors.
People:
Population: 89,258.
Ethnic groups: Black 82%, mixed black and European 13%, European and East
Indian 5% , and trace of Arawak/Carib Amerindian.
Religions: Roman Catholic 53%, Anglican 13.8%, other Protestant 33.2%
Languages: English (official), French patois.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional monarchy with Westminster-style parliament.
Capital: Saint George's.
Independence: 7 February 1974 (from UK).
Economy overview:
Grenada relies on tourism as its main source of foreign exchange, especially
since the construction of an international airport in 1985. Strong performances
in construction and manufacturing, together with the development of an offshore
financial industry, have also contributed to growth in national output.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 7.7%, industry: 23.9%, services:
68.4%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 27,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 976.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 13.
Radios: 57,000.
Television broadcast stations: 2.
Televisions: 33,000.
Internet users: 5,200.
Highways: Total: 1,040 km, paved: 638 km, unpaved: 402 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 3.
Return to Visiting Locations
|