|
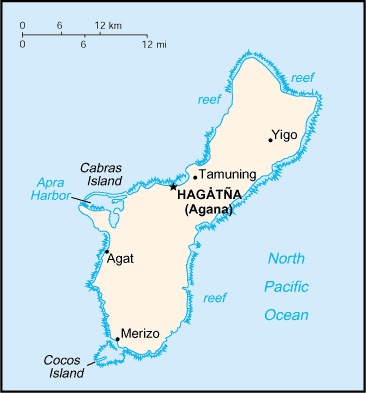
Guam
Background:
Guam was ceded to the US by Spain in 1898. Captured by the Japanese
in 1941, it was retaken by the US three years later. The military installation
on the island is one of the most strategically important US bases in the
Pacific.
Location:
Oceania, island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of
the way from Hawaii to the Philippines
Area: Total: 549 sq km.
Area - comparative: Three times the size of Washington, DC
Coastline: 125.5 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical marine; generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast
trade winds; dry season from January to June, rainy season from July to
December; little seasonal temperature variation.
Terrain: Volcanic origin, surrounded by coral reefs; relatively flat coralline
limestone plateau (source of most fresh water), with steep coastal cliffs and
narrow coastal plains in north, low-rising hills in center, mountains in south.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Mount
Lamlam 406 m.
Natural resources: Fishing (largely undeveloped), tourism (especially from
Japan).
Land use: Arable land: 11% permanent crops: 11% permanent pastures: 15%
forests and woodland: 18% other: 45%.
People:
Population: 157,557.
Ethnic groups: Camorra 47%, Filipino 25%, white 10%, Chinese, Japanese, Korean,
and other 18%.
Religions: Roman Catholic 85%, other 15%.
Languages: English, Chamorro, Japanese.
Government:
Capital: Hagatna (Agana).
Administrative divisions: None (territory of the US)
Economy overview:
The economy depends on US military spending, tourism, and
the export of fish and handicrafts. Total US grants, wage payments, and
procurement outlays amounted to $1 billion in 1998. Over the past 20 years, the
tourist industry has grown rapidly, creating a construction boom for new hotels
and the expansion of older ones. More than 1 million tourists visit Guam each
year; the Japanese normally make up almost 90% of the tourists.
Most food and industrial goods are imported. Guam faces the problem of building
up the civilian economic sector to offset the impact of military downsizing.
Labor force: 60,000 (2000 est.)
Labor force - by occupation: federal and territorial government 26%, private
74% (trade 24%, other services 40%, industry 10%) (2000 est.)
Industries: US military, tourism, construction, transshipment services,
concrete products, printing and publishing, food processing, textiles
Agriculture - products: Fruits, copra, vegetables; eggs, pork, poultry, beef
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 84,134.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 55,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 4, FM 7.
Radios: 221,000.
Television broadcast stations: 5.
Televisions: 106,000.
Internet users: 5,000.
Highways: Total: 885 km paved: 675 km unpaved: 210 km.
Airports: with paved runways: 4, with unpaved runways: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

