|
Guinea-Bissau
Background:
In 1994, 20 years after independence from Portugal, the country's first
multiparty legislative and presidential elections were held. An army uprising
that triggered a bloody civil war in 1998 created hundreds of thousands of
displaced persons. A military junta ousted the president in May 1999. An
interim government turned over power in February 2000 when opposition leader
Kumba Yala took office following two rounds of transparent presidential
elections. Guinea-Bissau's transition back to democracy will be complicated by
its crippled economy, devastated in the civil war.
Location:
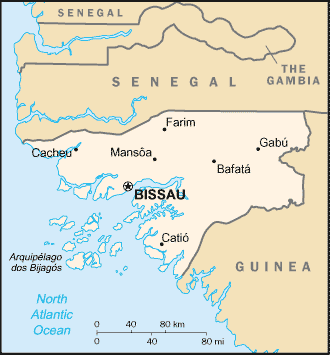
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea
and Senegal.
Area: Total: 36,120 sq km, water: 8,120 sq km, land: 28,000 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly less than three times the size of Connecticut.
Land boundaries: Total: 724 km border countries: Guinea 386 km, Senegal 338
km.
Coastline: 350 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June
to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with
northeasterly harmattan winds.
Terrain: Mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east.
Natural resources: Fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, unexploited deposits of
petroleum.
People:
Population: 1,360,827.
Ethnic groups: African 99% (Balanta 30%, Fula 20%, Manjaca 14%, Mandinga 13%,
Papel 7%), European and mulatto less than 1%.
Religions: Indigenous beliefs 50%, Muslim 45%, Christian 5%.
Languages: Portuguese (official), Crioulo, African languages.
Government:
Government type: Republic, multiparty since mid-1991.
Capital: Bissau.
Independence: 24 September 1973 (unilaterally declared by Guinea-Bissau); 10
September 1974 (recognized by Portugal).
Economy overview:
One of the 10 poorest countries in the world, Guinea-Bissau depends mainly on
farming and fishing. Cashew crops have increased remarkably in recent years,
and the country now ranks sixth in cashew production. Guinea-Bissau exports
fish and seafood along with small amounts of peanuts, palm kernels, and timber.
Rice is the major crop and staple food. However, intermittent fighting between
Senegalese-backed government troops and a military junta destroyed much of the
country's infrastructure and caused widespread damage to the economy in 1998;
the civil war led to a 28% drop in GDP that year, with partial recovery in
1999-2002.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 10,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1 (transmitter out of service), FM 4.
Radios: 49,000.
Internet users: 4,000.
Railways: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 4,400 km, paved: 453 km, unpaved: 3,947 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 3,
with unpaved runways: 25.
Return to Visiting Locations
|