|
Iceland
Background:
Settled by Norwegian and Celtic (Scottish and Irish) immigrants during the late
9th and 10th centuries A.D., Iceland boasts the world's oldest functioning
legislative assembly, the Althing, established in 930. Independent for over 300
years, Iceland was subsequently ruled by Norway and Denmark. Fallout from the
Askja volcano of 1875 devastated the Icelandic economy and caused widespread
famine. Over the next quarter century, 20% of the island's population
emigrated, mostly to Canada and the US. Limited home rule from Denmark was
granted in 1874 and complete independence attained in 1944. Literacy,
longevity, income, and social cohesion are first-rate by world standards.
Location:
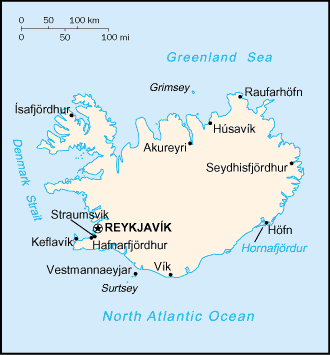
Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the North
Atlantic Ocean, northwest of the UK.
Area: Total: 103,000 sq km, water: 2,750 sq km, land: 100,250 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Kentucky
Coastline: 4,988 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters;
damp, cool summers.
Terrain: Mostly plateau interspersed with mountain peaks, icefields; coast
deeply indented by bays and fiords.
Natural resources: Fish, hydropower, geothermal power, diatomite.
People:
Population: 279,384.
Ethnic groups: Homogeneous mixture of descendants of Norse and Celts.
Religions: Evangelical Lutheran 93%.
Languages: Icelandic.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional republic.
Capital: Reykjavik.
Independence: 17 June 1944 (from Denmark).
Economy overview:
Iceland's Scandinavian-type economy is basically capitalistic, yet with an
extensive welfare system, low unemployment, and remarkably even distribution of
income. In the absence of other natural resources (except for abundant
hydrothermal and geothermal power), the economy depends heavily on the fishing
industry, providing 70% of export earnings and employing 12% of the work force.
The economy remains sensitive to declining fish stocks as well as to drops in
world prices for its main exports: fish and fish products, aluminum, and
ferrosilicon. The center-right government plans to continue its policies of
reducing the budget and current account deficits, limiting foreign borrowing,
containing inflation, revising agricultural and fishing policies, diversifying
the economy, and privatizing state-owned industries. The government remains
opposed to EU membership, primarily because of Icelanders' concern about losing
control over their fishing resources. I
Statistics:
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 15% (includes fishing 13%),
industry: 21%, services: 64%.
Telephones - main lines in use: 168,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 65,746.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 3, FM about 70.
Radios: 260,000.
Television broadcast stations: 14.
Televisions: 98,000.
Internet users: 168,000.
Railways: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 12,691 km paved: 3,262 km unpaved: 9,429 km.
Airports: 86.
Airports - with paved runways: 13, with unpaved runways: 73.
Return to Visiting Locations
|