|
Japan
Background:
While retaining its time-honored culture, Japan rapidly absorbed Western
technology during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. After its devastating
defeat in World War II, Japan recovered to become the second most powerful
economy in the world and a staunch ally of the US. While the emperor retains
his throne as a symbol of national unity, actual power rests in networks of
powerful politicians, bureaucrats, and business executives. The economy
experienced a major slowdown in the 1990s following three decades of
unprecedented growth.
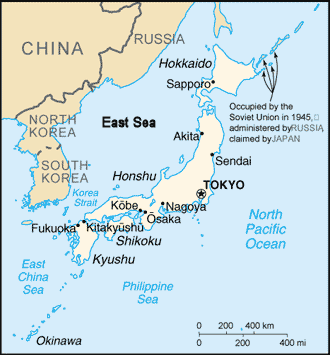
Location:
Eastern Asia, island chain between the North Pacific Ocean and the Sea of
Japan, east of the Korean Peninsula.
Area: Total: 377,835 sq km, note: includes Bonin Islands, Daito-shoto,
Minami-jima, Okino-tori-shima, Ryukyu Islands, and Volcano Islands, water:
3,091 sq km, land: 374,744 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than California.
Coastline: 29,751 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Varies from tropical in south to cool temperate in north.
Terrain: mostly rugged and mountainous
People:
Population: 126,974,628.
Ethnic groups: Japanese 99%, others 1% (Korean 51,126, Chinese 24,424,
Brazilian 18,223, Filipino 8,995, other 23,792).
Religions: Observe both Shinto and Buddhist 84%, other 16% (including Christian
0.7%).
Languages: Japanese.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government.
Capital: Tokyo.
Independence: 660 BC (traditional founding by Emperor Jimmu).
Economy overview:
Government-industry cooperation, a strong work ethic, mastery of high
technology, and a comparatively small defense allocation (1% of GDP) have
helped Japan advance with extraordinary rapidity to the rank of second most
technologically powerful economy in the world after the US and third largest
economy in the world after the US and China. A second basic feature has been
the
guarantee of lifetime employment for a substantial portion of the urban labor
force. The much
smaller agricultural sector is highly subsidized and protected, with crop
yields among the highest in the world. Usually self-sufficient in rice, Japan
must import about 50% of its requirements of other grain and fodder crops.
Japan maintains one of the world's largest fishing fleets and accounts for
nearly 15% of the global catch. For three decades overall real economic growth
had been spectacular: a 10% average in the 1960s, a 5% average in the 1970s,
and a 4% average in the 1980s.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 2%, industry: 36%, services: 62%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 60,381,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 63.88 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 215 plus 370 repeaters, FM 89 plus 485 repeaters,
shortwave 21.
Radios: 120.5 million.
Television broadcast stations: 211 plus 7,341 repeaters.
Televisions: 86.5 million.
Internet users: 47.08 million.
Railways: Total: 23,654 km.
Highways: Total: 1,152,207 km, paved: 863,003 km, unpaved: 289,204 km.
Airports: 173, with paved runways: 142, with unpaved runways: 31.
Heliports: 16.
Return to Visiting Locations
|