|
Macedonia
Background:
International recognition of The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia's
(F.Y.R.O.M.) independence from Yugoslavia in 1991 was delayed by Greece's
objection to the new state's use of what it considered a Hellenic name and
symbols. Greece finally lifted its trade blockade in 1995, and the two
countries agreed to normalize relations, despite continued disagreement over
F.Y.R.O.M.'s use of "Macedonia." F.Y.R.O.M.'s large Albanian minority, an
ethnic Albanian armed insurgency in F.Y.R.O.M. in 2001, and the status of
neighboring Kosovo continue to be sources of ethnic tension.
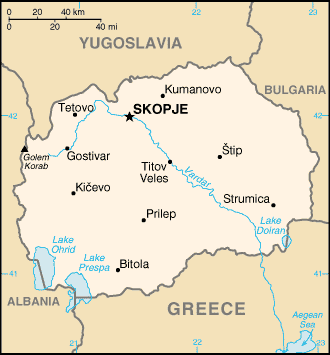
Location:
Southeastern Europe, north of Greece.
Area: Total: 25,333 sq km, water: 477 sq km. land: 24,856 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than Vermont.
Land boundaries: Total: 766 km, border countries: Albania 151 km, Bulgaria 148
km, Greece 246 km, Yugoslavia 221 km.
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked).
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Warm, dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy
snowfall.
Terrain: Mountainous territory covered with deep basins and valleys; three
large lakes, each divided by a frontier line; country bisected by the Vardar
River.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Vardar River 50 m, highest point: Golem
Korab (Maja e Korabit) 2,753 m.
Natural resources: Chromium, lead, zinc, manganese, tungsten, nickel, low-grade
iron ore, asbestos, sulfur, timber, arable land.
People:
Population: 2,054,800.
Ethnic groups: Macedonian 66.6%, Albanian 22.7%, Turkish 4%, Roma 2.2%, Serb
2.1%, other 2.4% .
Religions: Macedonian Orthodox 67%, Muslim 30%, other 3%.
Languages: Macedonian 70%, Albanian 21%, Turkish 3%, Serbo-Croatian 3%, other
3%.
Government:
Government type: Emerging democracy.
Capital: Skopje.
Independence: 17 September 1991 (from Yugoslavia).
Economy overview:
At independence in November 1991, Macedonia was the least developed of the
Yugoslav republics, producing a mere 5% of the total federal output of goods
and services. The collapse of Yugoslavia ended transfer payments from the
center and eliminated advantages from inclusion in a de facto free trade area.
An absence of infrastructure, UN sanctions on Yugoslavia, one of its largest
markets, and a Greek economic embargo over a dispute about the country's
constitutional name and flag hindered economic growth until 1996. GDP
subsequently rose each year through 2000. However, the leadership's commitment
to economic reform, free trade, and regional integration was undermined by the
ethnic Albanian insurgency of 2001.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 10%, industry: 32%., services: 58%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 408,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 12,362.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 29, FM 20.
Radios: 410,000.
Television broadcast stations: 31 (plus 166 repeaters).
Televisions: 510,000.
Internet users: 100,000.
Railways: Total: 699 km.
Highways: Total: 8,684 km, paved: 5,540 km, unpaved: 3,144 km.
Airports: 17, with paved runways: 10, with unpaved runways: 7.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

