|
Isle of Man
Background:
Part of the Norwegian Kingdom of the Hebrides until the 13th century when it
was ceded to Scotland, the isle came under the British crown in 1765. Current
concerns include reviving the almost extinct Manx Celtic language.
Location:
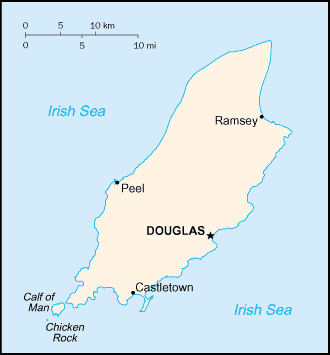
Location: Western Europe, island in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and
Ireland.
Area: Total: 572 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than three times the size of Washington, DC
Coastline: 160 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate; cool summers and mild winters; overcast about one-third of
the time.
Terrain: Hills in north and south bisected by central valley.
Natural resources: None.
Geography - note: One small islet, the Calf of Man, lies to the southwest, and
is a bird sanctuary.
People:
Population: 74,261.
Ethnic groups: Manx (Norse-Celtic descent), Briton.
Religions: Anglican, Roman Catholic, Methodist, Baptist, Presbyterian, Society
of Friends.
Languages: English, Manx Gaelic.
Government:
Dependency status: British crown dependency.
Government type: Parliamentary democracy.
Capital: Douglas.
Economy overview:
Offshore banking, manufacturing, and tourism are key sectors of the economy.
The government's policy of offering incentives to high-technology companies and
financial institutions to locate on the island has paid off in expanding
employment opportunities in high-income industries. As a result, agriculture
and fishing, once the mainstays of the economy, have declined in their shares
of GDP. Trade is mostly with the UK. The Isle of Man enjoys free access to EU
markets.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 1%, industry: 13%, services: 86%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 51,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 1.
Radios: NA
Television broadcast stations: 0 (receives broadcasts from the UK and
satellite).
Televisions: 27,490.
Railways: Total: 60 km.
Highways: Total: 800 km, paved: 800 km.
Airports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|