|
Micronesia
Background:
In 1979 the Federated States of Micronesia, a UN Trust Territory under US
administration, adopted a constitution. In 1986 independence was attained under
a Compact of Free Association with the US. Present concerns include large-scale
unemployment, over fishing, and over dependence on US aid.
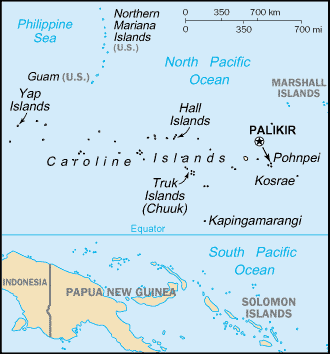
Location:
Oceania, island group in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the
way from Hawaii to Indonesia.
Area: Total: 702 sq km, note: includes Pohnpei (Ponape), Truk (Chuuk) Islands,
Yap Islands, and Kosrae, water: 0 sq km, land: 702 sq km.
Area - comparative: Four times the size of Washington, DC.
Land boundaries: 0 km.
Coastline: 6,112 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; heavy year-round rainfall, especially in the eastern
islands; located on southern edge of the typhoon belt with occasionally severe
damage.
Terrain: Islands vary geologically from high mountainous islands to low, coral
atolls; volcanic outcroppings on Pohnpei, Kosrae, and Truk.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Dolohmwar
(Totolom) 791 m.
Natural resources: Forests, marine products, deep-seabed minerals.
People:
Population: 135,869.
Ethnic groups: Nine ethnic Micronesian and Polynesian groups.
Religions: Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant 47%.
Languages: English (official and common language), Trukese, Pohnpeian, Yapese,
Kosrean, Ulithian, Woleaian, Nukuoro, Kapingamarangi.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional government in free association with the US; the
Compact of Free Association entered into force 3 November 1986 and is due for
renegotiation.
Capital: Palikir.
Independence: 3 November 1986 (from the US-administered UN Trusteeship).
Economy overview:
Economic activity consists primarily of subsistence farming and fishing. The
islands have few mineral deposits worth exploiting, except for high-grade
phosphate. The potential for a tourist industry exists, but the remote location
and a lack of adequate facilities hinder development. In 1996, the country
experienced a 20% reduction in revenues from the Compact of Free Association -
the agreement with the US in which Micronesia received $1.3 billion in
financial and technical assistance over a 15-year period until 2001. Since
these revenues accounted for 57% of consolidated government revenues, reduced
Compact funding resulted in a severe depression. Economic activity recovered in
1999-2001. The country's medium-term economic outlook appears fragile due to
likely further reductions in external grants made under the US Compact funding.
Geographical isolation and a poorly developed infrastructure remain major
impediments to long-term growth.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 50%, industry: 4%, services: 46%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 11,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 5, FM 1, shortwave 0.
Radios: 9,400.
Television broadcast stations: 2.
Televisions: 2,800.
Internet users: 2,000.
Highways: Total: 240 km, paved: 42 km, unpaved: 198 km.
Airports: 7, with paved runways: 6, with unpaved runways: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

