|
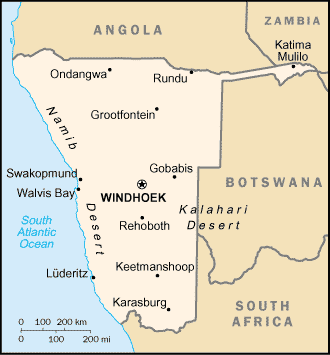
Namibia
Background:
South Africa occupied the German colony of South-West Africa during
World War I and administered it as a mandate until after World War II when it
annexed the territory. In 1988 that South Africa
agreed to end its administration in accordance with a UN peace plan for the
entire region. Independence came in 1990.
Location:
Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola
and South Africa
Area: Total: 825,418 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than half the size of Alaska
Land boundaries: Total: 3,936 km border countries: Angola 1,376 km, Botswana
1,360 km, South Africa 967 km, Zambia 233 km
Coastline: 1,572 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Desert; hot, dry; rainfall sparse and erratic.
Terrain: Mostly high plateau; Namib Desert along coast; Kalahari Desert in
east.
Natural resources: Diamonds, copper, uranium, gold, lead, tin, lithium,
cadmium, zinc, salt, vanadium, natural gas, hydropower, fish note: suspected
deposits of oil, coal, and iron ore.
People:
Population: 1,820,916.
Ethnic groups: Black 87.5%, white 6%, mixed 6.5% note: about 50% of the
population belong to the Ovambo tribe and 9% to the Kavangos tribe; other
ethnic groups are: Herero 7%, Damara 7%, Nama 5%, Caprivian 4%, Bushmen 3%,
Baster 2%, Tswana 0.5%.
Religions: Christian 80% to 90%, indigenous beliefs 10% to 20%
Languages: English 7% (official), Afrikaans common language of most of the
population and about 60% of the white population, German 32%, indigenous
languages: Oshivambo, Herero, Nama
Government:
Government type: republic
Capital: Windhoek
Economy overview:
The economy is heavily dependent on the extraction and
processing of minerals for export. Mining accounts for 20% of GDP. Namibia is
the fourth-largest exporter of nonfuel minerals in Africa and the world's
fifth-largest producer of uranium. Rich alluvial diamond deposits make Namibia
a primary source for gem-quality diamonds. Namibia also produces large
quantities of lead, zinc, tin, silver, and tungsten. About half of the
population depends on agriculture (largely subsistence agriculture) for its
livelihood. Namibia must import some of its food. Although per capita GDP is
five times the per capita GDP of Africa's poorest countries, the majority of
Namibia's people live in pronounced poverty because of large-scale
unemployment, the great inequality of income distribution, and the large amount
of wealth going to foreigners.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 110,200.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 82,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 39.
Radios: 232,000.
Television broadcast stations: 8 (plus about 20 low-power repeaters).)
Televisions: 60,000.
Internet users: 30,000.
Railways: Total: 2,382 km narrow gauge: 2,382 km 1.067-m gauge.
Highways: Paved: 5,378 km, unpaved: 59,430 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 22 - with unpaved runways: 115 .
Return to Visiting Locations
|

