|
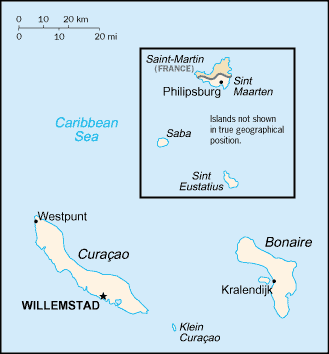
Netherlands Antilles
Background:
Once the center of the Caribbean slave trade, the island of Curacao was hard
hit by the abolition of slavery in 1863. Its prosperity (and that of
neighboring Aruba) was restored in the early 20th century with the construction
of oil refineries to service the newly discovered Venezuelan oil fields. The
island of Saint Martin is shared with France; its northern portion is named
Saint-Martin and is part of Guadeloupe, and its southern portion is named Sint
Maarten and is part of the Netherlands Antilles.
Location:
Location: Caribbean, two island groups in the Caribbean Sea - one includes
Curacao and Bonaire north of Venezuela; the other is east of the Virgin
Islands.
Area: Total: 960 sq km, note: includes Bonaire, Curacao, Saba, Saint
Eustatius, and Saint Maarten (Dutch part of the island of Saint Martin).
Area - comparative: More than five times the size of Washington, DC.
Land boundaries: Total: 10.2 km, border countries: Guadeloupe (Saint Martin)
10.2 km.
Coastline: 364 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; ameliorated by northeast trade winds.
Terrain: Generally hilly, volcanic interiors.
Natural resources: Phosphates (Curacao only), salt (Bonaire only.)
People:
Population: 216,226 .
Ethnic groups: Mixed black 85%, Carib Amerindian, white, East Asian.
Religions: Roman Catholic, Protestant, Jewish, Seventh-Day Adventist.
Languages: Dutch (official), Papiamento (a Spanish-Portuguese-Dutch-English
dialect) predominates, English widely spoken, Spanish.
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary
Capital: Willemstad.
Dependency status: Part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands; full autonomy in
internal affairs granted in 1954; Dutch Government responsible for defense and
foreign affairs.
Economy overview:
Tourism, petroleum refining, and offshore finance are the mainstays of this
small economy, which is closely tied to the outside world. Although GDP has
declined or remained even in each of the past six years, the islands enjoy a
high per capita income and a well-developed infrastructure compared with other
countries in the region. Almost all consumer and capital goods are imported,
the US and Mexico being the major suppliers. Poor soils and inadequate water
supplies hamper the development of agriculture.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 76,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 13,977.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 9, FM 4.
Radios: 217,000.
Television broadcast stations: 3 (there is also a cable service, which supplies
programs received from various US satellite networks and two Venezuelan
channels).
Televisions: 69,000.
Internet users: 2,000.
Highways: Total: 600 km, paved: 300 km, unpaved: 300 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 5.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

