|
New Zealand
Background:
The British colony of New Zealand became an independent dominion in 1907 and
supported the UK militarily in both World Wars. New Zealand's full
participation in number of defense alliances lapsed by the 1980s. In recent
years the government has sought to address longstanding native Maori grievances.
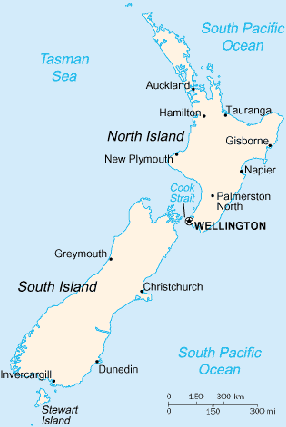
Location:
Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia
Area: Total: 268,680 sq km, note: includes Antipodes Islands, Auckland
Islands, Bounty Islands, Campbell Island, Chatham Islands, and Kermadec
Islands, water: NA sq km, land: NA sq km.
Area - comparative: About the size of Colorado.
Coastline: 15,134 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate with sharp regional contrasts.
Terrain: Predominately mountainous with some large coastal plains.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Mount Cook
3,764 m.
Natural resources: Natural gas, iron ore, sand, coal, timber, hydropower, gold,
limestone.
People:
Population: 3,908,037.
Ethnic groups: New Zealand European 74.5%, Maori 9.7%, other European 4.6%,
Pacific Islander 3.8%, Asian and others 7.4%.
Religions: Anglican 24%, Presbyterian 18%, Roman Catholic 15%, Methodist 5%,
Baptist 2%, other Protestant 3%, unspecified or none 33%.
Languages: English (official), Maori (official).
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary democracy.
Capital: Wellington.
Dependent areas: Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau.
Independence: 26 September 1907 (from UK.)
Economy overview:
Since 1984 the government has accomplished major economic restructuring,
transforming New Zealand from an agrarian economy dependent on concessionary
British market access to a more industrialized, free market economy that can
compete globally. This dynamic growth has boosted real incomes (but left behind
many at the bottom of the ladder), broadened and deepened the technological
capabilities of the industrial sector, and contained inflationary pressures.
While per capita incomes have been rising, however, they remain below the level
of the four largest EU economies, and there is some government concern that New
Zealand is not closing the gap. New Zealand is heavily dependent on trade -
particularly in agricultural products - to drive growth, and it has been
affected by the global economic slowdown and the slump in commodity prices.
Thus far the New Zealand economy has been relatively resilient, achieving about
3% growth in 2001, but the New Zealand business cycle tends to lag the US cycle
by about six months, so the worst of the downturn may not hit until mid-2002.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 8%, industry: 23%, services: 69%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1.92 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 2.2 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 124, FM 290, shortwave 4.
Radios: 3.75 million.
Television broadcast stations: 41 (plus 52 medium-power repeaters and over 650
low-power repeaters).
Televisions: 1.926 million.
Internet users: 1.78 million.
Railways: Total: 3,908 km.
Highways: Total: 92,200 km, paved: 53,568 km, unpaved: 38,632 km.
Airports: 106, with paved runways: 44, with unpaved runways: 62.
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|