|
Nicaragua
Background:
Settled as a colony of Spain in the 1520s, Nicaragua gained its independence in
1821. Violent opposition to governmental manipulation and corruption spread to
all classes by 1978 and resulted in a short-lived civil war that brought the
Marxist Sandinista guerrillas to power in 1979. Nicaraguan aid to leftist
rebels in El Salvador caused the US to sponsor anti-Sandinista contra
guerrillas through much of the 1980s. Free elections in 1990, 1996, and again
in 2001 saw the Sandinistas defeated. The country has slowly rebuilt its
economy during the 1990s, but was hard hit by Hurricane Mitch in 1998.
Location:
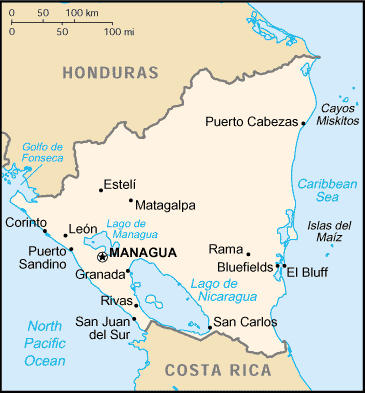
Middle America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean,
between Costa Rica and Honduras.
Area: total: 129,494 sq km, water: 9,240 sq km, land: 120,254 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than the state of New York.
Land boundaries: Total: 1,231 km, border countries: Costa Rica 309 km,
Honduras 922 km.
Coastline: 910 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical in lowlands, cooler in highlands.
Terrain: Extensive Atlantic coastal plains rising to central interior
mountains; narrow Pacific coastal plain interrupted by volcanoes.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Mogoton
2,438 m.
Natural resources: Gold, silver, copper, tungsten, lead, zinc, timber, fish.
People:
Population: 5,023,818.
Ethnic groups: Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 69%, white 17%, black 9%,
Amerindian 5%.
Religions: Roman Catholic 85%, Protestant.
Languages: Spanish (official), note: English and indigenous languages on
Atlantic coast.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Managua.
Independence: 15 September 1821 (from Spain).
Economy overview:
Nicaragua, one of the hemisphere's poorest countries, faces low per capita
income, flagging socio-economic indicators, and huge external debt.
Distribution of income is extremely unequal. While the country has made
progress toward macroeconomic stabilization over the past few years, a banking
crisis and scandal has shaken the economy. Managua will continue to be
dependent on international aid and debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor
Countries (HIPC) initiative. Donors have made aid conditional on improving
governability, the openness of government financial operation, poverty
alleviation, and human rights. Nicaragua met the conditions for additional debt
service relief in December 2000. Growth should move up in 2002 because of
increased private investment and recovery in the global economy.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 33%, industry: 23%, services: 44%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 140,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 7,911.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 63, FM 32, shortwave 1.
Radios: 1.24 million.
Television broadcast stations: 3 (plus seven low-power repeaters).
Televisions: 320,000.
Internet users: 20,000.
Railways: Total: 6 km.
Highways: Total: 16,382 km, paved: 1,818 km, unpaved: 14,564 km.
Airports: 182, with paved runways: 11, with unpaved runways: 171.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

