|
Norway
Background:
Despite its neutrality, Norway was not able to avoid occupation by Germany in
World War II. In 1949, neutrality was abandoned and Norway became a member of
NATO. Discovery of oil and gas in adjacent waters in the late 1960s boosted
Norway's economic fortunes. The current focus is on containing spending on the
extensive welfare system and planning for the time when petroleum reserves are
depleted. In referenda held in 1972 and 1994, Norway rejected joining the EU.
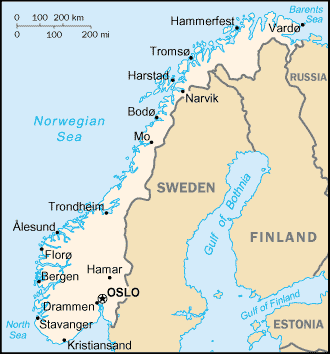
Location:
Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of
Sweden.
Area: Total: 324,220 sq km, land: 307,860 sq km, water: 16,360 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than New Mexico.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,544 km, border countries: Finland 729 km, Sweden
1,619 km, Russia 196 km.
Coastline: 21,925 km (includes mainland 3,419 km, large islands 2,413 km, long
fjords, numerous small islands, and minor indentations 16,093 km).
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate along coast, modified by North Atlantic Current; colder
interior with increased precipitation and colder summers; rainy year-round on
west coast.
Terrain: Glaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile
valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic
tundra in north.
Natural resources: Petroleum, copper, natural gas, pyrites, nickel, iron ore,
zinc, lead, fish, timber, hydropower.
People:
Population: 4,525,116.
Ethnic groups: Norwegian, Sami 20,000.
Religions: Evangelical Lutheran 86% (state church), other Protestant and Roman
Catholic 3%, other 1%, none and unknown 10%.
Languages: Norwegian (official), note: small Sami- and Finnish-speaking
minorities.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional monarchy.
Capital: Oslo.
Independence: 7 June 1905 Norway declared the union with Sweden dissolved; 26
Economy overview:
October 1905 Sweden agreed to the repeal of the union.
The Norwegian economy is a prosperous bastion of welfare capitalism, featuring
a combination of free market activity and government intervention. The
government controls key areas, such as the vital petroleum sector (through
large-scale state enterprises). The country is richly endowed with natural
resources - petroleum, hydropower, fish, forests, and minerals - and is highly
dependent on its oil production and international oil prices; in 1999, oil and
gas accounted for 35% of exports. Only Saudi Arabia and Russia export more oil
than Norway. Oslo opted to stay out of the EU during a referendum in November
1994. The government moved ahead with privatization in
2000, even proposing the sale of up to one-third of the 100% state-owned oil
company Statoil.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 2%, industry: 31%, services: 67%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 2.735 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 2,080,408.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 5, FM at least 650, shortwave 1.
Radios: 4.03 million.
Television broadcast stations: 360 (plus 2,729 repeaters).
Televisions: 2.03 million.
Internet users: 2.45 million.
Railways: Total: 4,006 km.
Highways: Total: 91,180 km, paved: 67,838 km, unpaved: 23,342 km .
Airports: 102, with paved runways: 67, with unpaved runways: 35.
Return to Visiting Locations
|