|
Singapore
Background:
Founded as a British trading colony in 1819, Singapore joined Malaysia in 1963,
but withdrew two years later and became independent. It subsequently became one
of the world's most prosperous countries, with strong international trading
links (its port is one of the world's busiest) and with per capita GDP equal to
that of the leading nations of Western Europe.
Location:
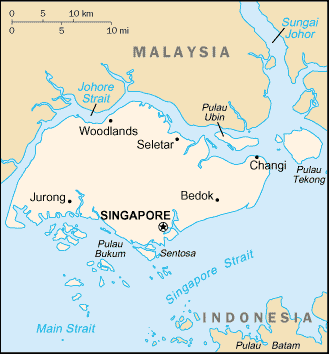
Southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia .
Area: Total: 692.7 sq km, water: 10 sq km. land: 682.7 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than 3.5 times the size of Washington, DC.
Coastline: 193 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; hot, humid, rainy; two distinct monsoon seasons -
Northeastern monsoon from December to March and Southwestern monsoon from June
to September; inter-monsoon - frequent afternoon and early evening
thunderstorms.
Terrain: Lowland; gently undulating central plateau contains water catchment
area and nature preserve.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Singapore Strait 0 m, highest point: Bukit
Timah 166 m.
Natural resources: Fish, deepwater ports.
People:
Population: 4,452,732.
Ethnic groups: Chinese 76.7%, Malay 14%, Indian 7.9%, other 1.4%.
Religions: Buddhist (Chinese), Muslim (Malays), Christian, Hindu, Sikh, Taoist,
Confucianist.
Languages: Chinese (official), Malay (official and national), Tamil (official),
English (official).
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary republic.
Capital: Singapore.
Independence: 9 August 1965 (from Malaysia).
Economy overview:
Singapore, a highly developed and successful free-market economy, enjoys a
remarkably open and corruption-free environment, stable prices, and one of the
highest per capita GDPs in the world. The economy depends heavily on exports,
particularly in electronics and manufacturing, and was hard hit in 2001 by the
global recession and the slump in the technology sector. In 2001, GDP
contracted by 2.2%. The economy is expected to recover in 2002 in response to
improvements in the US economy, and GDP growth for 2002 is projected to be 3%
to 4%. In the longer term the government hopes to establish a new growth path
that will be less vulnerable to the external business cycle than the current
export-led model, but is unlikely to abandon efforts to establish Singapore as
Southeast Asia's financial and high-tech hub.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 0%, industry: 33%, services: 67%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1.95 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 2.74 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 0, FM 16, shortwave 2.
Radios: 2.6 million.
Television broadcast stations: 6.
Televisions: 1.33 million.
Internet users: 2.12 million.
Railways: Total: 38.6 km.
Highways: Total: 3,150 km, paved: 3,066 km, unpaved: 84 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 9.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

