|
Sweden
Background:
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden has not participated in any
war in almost two centuries. An armed neutrality was preserved in both World
Wars. Sweden's long-successful economic formula of a capitalist system
interlarded with substantial welfare elements was challenged in the 1990s by
high unemployment, rising maintenance costs, and a declining position in world
markets. Indecision over the country's role in the political and economic
integration of Europe delayed Sweden's entry into the EU until 1995, and waived
the introduction of the euro in 1999.
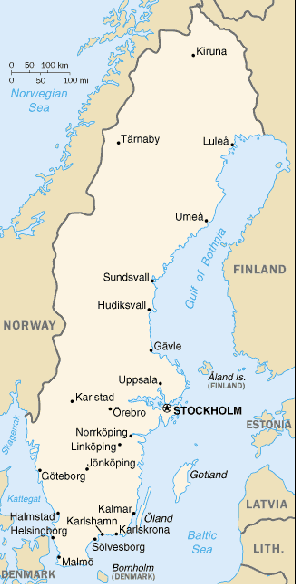
Location:
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and
Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway.
Area: Total: 449,964 sq km, water: 39,030 sq km, land: 410,934 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than California.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,205 km, border countries: Finland 586 km, Norway
1,619 km.
Coastline: 3,218 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy
summers; sub arctic in north.
Terrain: Mostly flat or gently rolling lowlands; mountains in west.
People:
Population: 8,876,744.
Ethnic groups: Indigenous population: Swedes and Finnish and Sami minorities;
foreign-born or first-generation immigrants: Finns, Yugoslavs, Danes,
Norwegians, Greeks, Turks.
Religions: Lutheran 87%, Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish,
Buddhist.
Languages: Swedish, note: small Sami- and Finnish-speaking minorities.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional monarchy.
Capital: Stockholm.
Independence: 6 June 1523 (Gustav Vasa elected king).
Economy overview:
Aided by peace and neutrality for the whole 20th century, Sweden has achieved
an enviable standard of living under a mixed system of high-tech capitalism and
extensive welfare benefits. It has a modern distribution system, excellent
internal and external communications, and a skilled labor force. Timber,
hydropower, and iron ore constitute the resource base of an economy heavily
oriented toward foreign trade. Privately owned firms account for about 90% of
industrial output, of which the engineering sector accounts for 50% of output
and exports. Agriculture accounts for only 2% of GDP and 2% of the jobs.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 6.017 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 3.835 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 265, shortwave 1.
Radios: 8.25 million.
Television broadcast stations: 169 (plus 1,299 repeaters).
Televisions: 4.6 million.
Internet users: 5.64 million.
Railways: Total: 12,821 km.
Highways: Total: 210,760 km, paved: 162,707 km, unpaved: 48,053 km.
Airports: 255, with paved runways: 147, with unpaved runways: 108.
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

