|

Tunisia
Background:
Following independence from France in 1956, President Habib BOURGUIBA
established a strict one-party state. He dominated the country for 31 years,
repressing Islamic fundamentalism and establishing rights for women unmatched
by any other Arab nation. In recent years, Tunisia has taken a moderate,
non-aligned stance in its foreign relations. Domestically, it has sought to
defuse rising pressure for a more open political society.
Location:
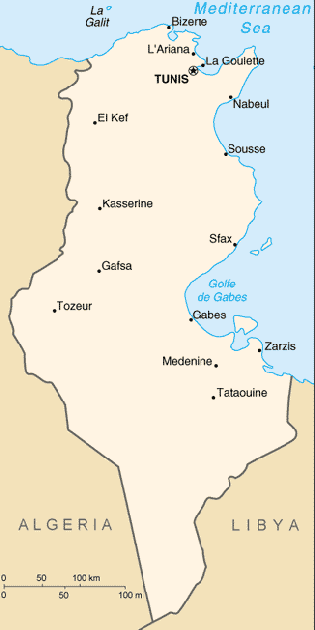
Location: Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Algeria and
Libya.
Area: total: 163,610 sq km, water: 8,250 sq km, land: 155,360 sq km.
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Georgia.
Land boundaries: Total: 1,424 km, border countries: Algeria 965 km, Libya 459
km.
Climate and Terrain:
Coastline: 1,148 km.
Climate: Temperate in north with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers;
desert in south.
Terrain: Mountains in north; hot, dry central plain; semiarid south merges into
the Sahara.
Natural resources: Petroleum, phosphates, iron ore, lead, zinc, salt.
People:
Population: 9,924,742.Ethnic groups: Arab 98%, European 1%, Jewish and other
1%.
Religions: Muslim 98%, Christian 1%, Jewish and other 1%.
Languages: Arabic (official and one of the languages of commerce), French
(commerce)
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Tunis.
Independence: 20 March 1956 (from France).
Economy overview:
Tunisia has a diverse economy, with important agricultural, mining, energy,
tourism, and manufacturing sectors. Governmental control of economic affairs
while still heavy has gradually lessened over the past decade with increasing
privatization, simplification of the tax structure, and a prudent approach to
debt. Real growth averaged 5.4% in 1997-2001 but slowed to 1.9% in 2002 because
of agricultural drought, slow investment, and lackluster tourism. Increased
rainfall portends higher growth levels for 2003, but continued regional tension
from the war in Iraq will most likely continue to suppress tourism earnings.
Tunisia has agreed to gradually remove barriers to trade with the European
Union over the next decade. Broader privatization, further liberalization of
the investment code to increase foreign investment, improvements in government
efficiency, and reduction of the trade deficit are among the challenges for the
future.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 654,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 50,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 7, FM 20, shortwave 2.
Radios: 2.06 million.
Television broadcast stations: 26 (plus 76 repeaters).
Televisions: 920,000.
Internet users: 400,000.
Railways: Total: 2,152 km.
Highways: Total: 18,997 km, paved: 12,310 km, unpaved: 6,687 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 14,
with unpaved runways: 16.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

