|
Tuvalu
Background:
In 1974, ethnic differences within the British colony of the
Gilbert and Ellice Islands caused the Polynesians of the Ellice Islands to vote
for separation from the Micronesians of the Gilbert Islands. The following
year, the Ellice Islands became the separate British colony of Tuvalu.
Independence was granted in 1978. In 2000, Tuvalu negotiated a contract leasing
its Internet domain name ".tv" for $50 million in royalties over the next dozen
years.
Location:
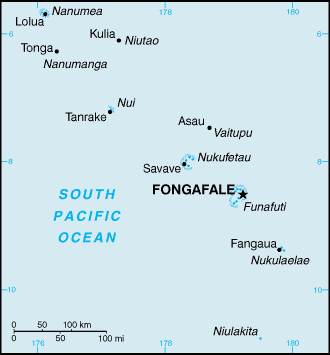
Oceania, island group consisting of nine coral atolls in the South
Pacific Ocean, about one-half of the way from Hawaii to Australia.
Geographic coordinates: 8 00 S, 178 00 E.
Area: total: 26 sq km.
Area - comparative: 0.1 times the size of Washington, DC.
Coastline: 24 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Tropical; moderated by easterly trade winds (March to November);
westerly gales and heavy rain (November to March).
Very low-lying and narrow coral atolls.
People:
Population: 10,991 (July 2001 est.).
Ethnic groups: Polynesian 96%.
Religions: Church of Tuvalu (Congregationalist) 97%, Seventh-Day Adventist
1.4%, Baha'i 1%, other 0.6%
Languages: Tuvaluan, English.
Government:
Capital: Funafuti. Government type: constitutional monarchy with a
parliamentary democracy; began debating republic status in 1992.
Independence: 1 October 1978 (from UK).
Economy overview:
Tuvalu consists of a densely populated, scattered group of
nine coral atolls with poor soil. The country has no known mineral resources
and few exports. Subsistence farming and fishing are the primary economic
activities. Government revenues largely come from the sale of stamps and coins
and worker remittances. About 1,000 Tuvaluans work in Nauru in the phosphate
mining industry. Nauru has begun repatriating Tuvaluans, however, as phosphate
resources decline. Substantial income is received annually from an
international trust fund established in 1987 by Australia, NZ, and the UK and
supported also by Japan and South Korea. Thanks to wise investments and
conservative withdrawals, this Fund has grown from an initial $17 million to
over $35 million in 1999. The US government is also a major revenue source for
Tuvalu, with 1999 payments from a 1988 treaty on fisheries at about $9 million,
a total that is expected to rise annually. In 1998, Tuvalu began deriving
revenue from use of its area code for "900" lines and in 2000, from the sale of
its ".tv" Internet domain name.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1,000 (1997).
Radiotelephone communications between islands
Radio broadcast stations: AM 1, FM 0.
Radios: 4,000 (1997).
Televisions: 800.
Internet country code: .tv
Railways: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 8 km. paved: 0 km. unpaved: 8 km.
Airports - with unpaved runways: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|