|

Vanuatu
Background:
The British and French, who settled the New Hebrides in the 19th century,
agreed in 1906 to an Anglo-French Condominium, which administered the islands
until independence in 1980.
Location:
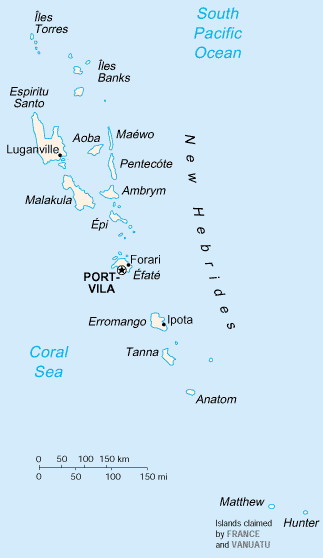
Location: Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about
three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to Australia.
Area: Total: 12,200 sq km, land: 12,200 sq km, note: includes more than 80
islands.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than Connecticut.
Coastline: 2,528 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; moderated by southeast trade winds.
Terrain: Mostly mountains of volcanic origin; narrow coastal plains.
Natural resources: Manganese, hardwood forests, fish.
Environment - current issues: A majority of the population does not have access
to a potable and reliable supply of water; deforestation.
Geography - note: A Y-shaped chain of four main islands and 80 smaller islands;
several of the islands have active volcanoes.
People:
Population: 199,414.
Ethnic groups: Indigenous Melanesian 98%, French, Vietnamese, Chinese, other
Pacific Islanders.
Religions: Presbyterian 36.7%, Anglican 15%, Roman Catholic 15%, indigenous
beliefs 7.6%, Seventh-Day Adventist 6.2%, Church of Christ 3.8%, other 15.7%
(including Jon Frum Cargo cult).
Languages: Three official languages: English, French, pidgin (known as Bislama
or Bichelama), plus more than 100 local languages.
Government:
Government type: Parliamentary republic.
Capital: Port-Vila.
Independence: 30 July 1980 (from France and UK).
Economy overview:
The economy is based primarily on subsistence or small-scale agriculture, which
provides a living for 65% of the population. Fishing, offshore financial
services, and tourism, with about 50,000 visitors in 1997, are other mainstays
of the economy. Mineral deposits are negligible; the country has no known
petroleum deposits. A small light industry sector caters to the local market.
Tax revenues come mainly from import duties. Economic development is hindered
by dependence on relatively few commodity exports, vulnerability to natural
disasters, and long distances from main markets and between constituent
islands. A severe earthquake in November 1999 followed by a tsunami, caused
extensive damage to the northern island of Pentecote and left thousands
homeless.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 5,500.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 310.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 2, shortwave 1.
Radios: 67,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 2,300.
Internet users: 3,000.
Railways: 0 km.
Highways: Total: 1,070 km, paved: 256 km, unpaved: 814 km.
Airports - with paved runways: 3, with unpaved runways: 27.
Return to Visiting Locations
|



