|
Venezuela
Background:
Venezuela was one of the three countries that emerged from the collapse of Gran
Colombia in 1830 (the others being Colombia and Ecuador). For most of the first
half of the 20th century, Venezuela was ruled by generally benevolent military
strongmen, who promoted the oil industry and allowed for some social reforms.
Democratically-elected governments have held sway since 1959. Current concerns
include: an embattled president who is losing his once solid support among
Venezuelans, a divided military, drug-related conflicts along the Colombian
border, increasing internal drug consumption, overdependence on the petroleum
industry with its price fluctuations, and irresponsible mining operations that
are endangering the rain forest and indigenous peoples.
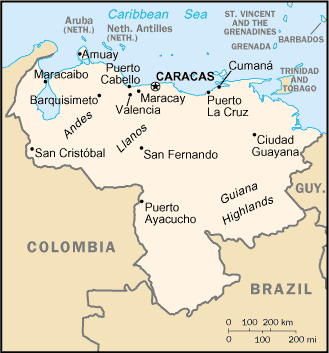
Location:
Northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic
Ocean, between Colombia and Guyana.
Area: Total: 912,050 sq km, land: 882,050 sq km, water: 30,000 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly more than twice the size of California.
Land boundaries: Total: 4,993 km, border countries: Brazil 2,200 km, Colombia
2,050 km, Guyana 743 km.
Coastline: 2,800 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands.
Terrain: Andes Mountains and Maracaibo Lowlands in northwest; central plains
(llanos); Guiana Highlands in southeast.
People:
Population: 24,287,670.
Ethnic groups: Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Arab, German, African, indigenous
people.
Religions: Nominally Roman Catholic 96%, Protestant 2%, other 2%.
Languages: Spanish (official), numerous indigenous dialects.
Government:
Government type: Federal republic.
Capital: Caracas.
Independence: 5 July 1811 (from Spain).
Economy overview:
The petroleum sector dominates the economy, accounting for roughly a third of
GDP, around 80% of export earnings, and more than half of government operating
revenues. Venezuelan officials estimate that GDP grew by 2.7% in 2001. A strong
rebound in international oil prices fueled the recovery from the steep
recession in 1999. Nevertheless, a weak non-oil sector and capital flight - and
a temporary fall in oil prices - undercut the recovery. In early 2002,
President Chavez changed the exchange rate regime from a crawling peg to a
free-floating exchange rate, causing the bolivar to depreciate significantly.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 5%, industry: 40%, services: 55%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 2.6 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 2 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 201, FM NA (20 in Caracas), shortwave 11.
Radios: 10.75 million.
Television broadcast stations: 66 (plus 45 repeaters).
Televisions: 4.1 million.
Internet users: 950,000.
Railways: total: 682 km.
Highways: Total: 96,155 km, paved: 32,308 km, unpaved: 63,847 km.
Airports: 372, with paved runways: 124, with unpaved runways: 248.
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

