|
Zambia
Background:
The South Africa Company administered the territory of Northern Rhodesia from
1891 until it was taken over by the UK in 1923. During the 1920s and 1930s,
advances in mining spurred development and immigration. The name was changed to
Zambia upon independence in 1964. In the 1980s and 1990s, declining copper
prices and a prolonged drought hurt the economy. Elections in 1991 brought an
end to one-party rule, but the subsequent vote in 1996 saw blatant harassment
of opposition parties. The election in 2001 was marked by administrative
problems with at least two parties filing legal petitions challenging the
results. Opposition parties currently hold a majority of seats in the National
Assembly.
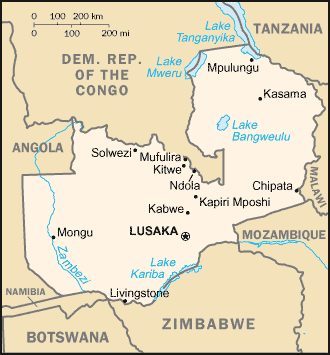
Location:
Southern Africa, east of Angola.
Area: Total: 752,614 sq km, water: 11,890 sq km, land: 740,724 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than Texas.
Land boundaries: Total: 5,664 km, border countries: Angola 1,110 km,
Democratic Republic of the Congo 1,930 km, Malawi 837 km, Mozambique 419 km,
Namibia 233 km, Tanzania 338 km, Zimbabwe 797 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical; modified by altitude; rainy season (October to April.)
Terrain: Mostly high plateau with some hills and mountains.
Natural resources: Copper, cobalt, zinc, lead, coal, emeralds, gold, silver,
uranium, hydropower.
People:
Population: 9,959,037.
Ethnic groups: African 98.7%, European 1.1%, other 0.2%.
Religions: Christian 50%-75%, Muslim and Hindu 24%-49%, indigenous beliefs 1%.
Languages: English (official), major vernaculars - Bemba, Kaonda, Lozi, Lunda,
Luvale, Nyanja, Tonga, and about 70 other indigenous languages.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Lusaka.
Independence: 24 October 1964 (from UK).
Economy overview:
Despite progress in privatization and budgetary reform, Zambia's economy has a
long way to go. Privatization of government-owned copper mines relieved the
government from covering mammoth losses generated by the industry and greatly
improved the chances for copper mining to return to profitability and spur
economic growth. However, low mineral prices have slowed the benefits from
privatizing the mines and reduced incentives for further private investment in
the sector. Unemployment rates remain
high, but GDP growth should continue at about 4%. Inflation should remain close
to 20%.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 24%, industry: 25%, services: 51%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 130,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 75,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 19, FM 5.
Radios: 1.2 million.
Television broadcast stations: 9.
Televisions: 277,000.
Internet users: 15,000.
Railways: Total: 2,157 km.
Highways: Total: 66,781 km.
Airports: with paved runways: 11, with unpaved runways: 100.
Return to Visiting Locations
|