|
Some Common Myths Thought to be True - Myth 65
Myth 65: Human Blood in Veins is Blue
Human blood in veins is not blue. In fact, blood is always red due to
hemoglobin. Deoxygenated blood has a deep red color, and oxygenated blood has a
light cherry-red color. The misconception probably arises for two reasons:
1. Veins appear blue because light, penetrating the skin, is absorbed and
reflected back to the eye. Since only the higher energy wavelengths can do this
(lower energy wavelengths just don't have the *oomph*), only higher energy
wavelengths are seen. And higher energy wavelengths are what we call "blue." In
an experiment, glass tubes were filled with blood and immersed in milk, milk
having a similar ratio of fat, proteins, and water in emulsion as skin. At a
certain depth, the tubes appeared blue.
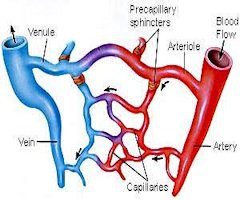
2. From the way diagrams use colors to show the difference between veins
(usually shown in blue) and arteries (usually shown in red).
|
|
There are three varieties of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
During blood circulation, the arteries carry blood away from the heart. The
capillaries connect the arteries to veins. Finally, the veins carry the blood
back to the heart. If you took all of the blood vessels out of an average
child, and laid them out in one line, the line would be over 60,000 miles long!
An adult's vessels would be closer to 100,000 miles long!
When we measure blood pressure, we use the blood flowing through the arteries
because it has a higher pressure than the blood in the veins. Your blood
pressure is measured using two numbers. The first number, which is higher, is
taken when the heart beats during the systole phase. The second number is taken
when the heart relaxes during the diastole phase. Those two numbers stand for
millimeters. A column of mercury rises and falls with the beat of the heart.
The height of the column is measured in millimeters. Normal blood pressure
ranges from 110 to 150 millimeters (as the heart beats) over 60 to 80
millimeters (as the heart relaxes). It is normal for your blood pressure to
increase when you are exercising and to decrease when you are sleeping. If your
blood pressure stays too high or too low, however, you may be at risk of heart
disease.
|
